SUMMARY
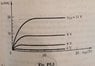
The values of K and VTR for the MOSFET are determined to be K = 0.25 mA/V² and VTR = 2V based on the v-I characteristics graph. The transition from triode to constant current is analyzed using the equation iD = K(VGS - VTR)². The VTR value is confirmed by identifying the point where the graph becomes horizontal, specifically at VGS = 4V. Additionally, using multiple curves allows for simultaneous calculations of K and VTR, ensuring accuracy in determining these parameters.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of MOSFET operation and characteristics
- Familiarity with the equation iD = K(VGS - VTR)²
- Knowledge of the different operating regions of MOSFETs (triode, saturation)
- Ability to interpret v-I characteristic graphs
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation and application of the equation iD = K(VGS - VTR)²
- Learn how to analyze MOSFET v-I characteristics in different operating regions
- Explore the impact of VGS and VDS on MOSFET performance
- Investigate methods for extracting K and VTR values from characteristic curves
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, students studying semiconductor devices, and professionals involved in MOSFET design and analysis will benefit from this discussion.