SUMMARY
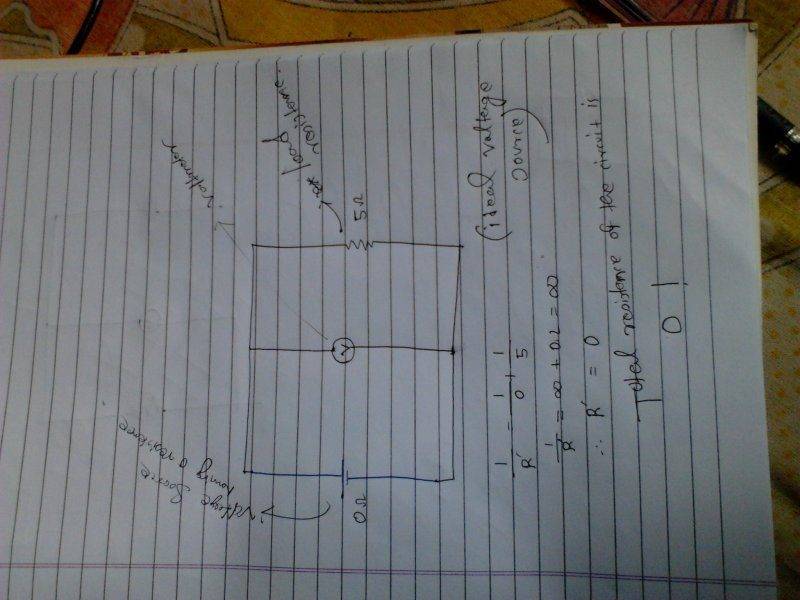
The total resistance of a circuit with an ideal voltage source is effectively zero ohms when considering the source's internal resistance. An ideal voltage source maintains a constant voltage regardless of the load, which means its internal resistance is zero. When calculating total resistance, one must clarify whether the components are in series or parallel, as this affects the measurement. The discussion emphasizes the importance of defining the measurement points and understanding the distinction between DC and AC analysis.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of ideal voltage sources
- Knowledge of Thevenin's theorem
- Familiarity with AC and DC circuit analysis
- Basic concepts of resistance and impedance
NEXT STEPS
- Study Thevenin equivalent circuits in detail
- Learn about AC circuit analysis techniques
- Explore the concept of equivalent impedance in circuits
- Review the principles of voltage measurement across circuit components
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, circuit designers, students studying electronics, and anyone interested in understanding the behavior of ideal voltage sources in circuits.