- #1
Shakattack12
- 24
- 2
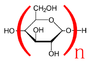
Hey guys. When a polysaccharide (e.g. starch) is made I understand that monosaccharides are linked together and a water molecule is removed. In the final product the polysaccharide has a mass of n times its empirical formula plus a water molecule. Like the mass of 300 starches from 300 glucose molecules is 300(C6H10O5) + H2O. Why is this?