Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the nature of intermolecular forces in carbon dioxide (CO2) molecules, particularly focusing on the roles of dipole-dipole interactions, quadrupole interactions, and London dispersion forces. Participants explore the implications of molecular geometry and charge distribution on these forces, comparing CO2 with other molecules like O2 and CSe2.
Discussion Character
- Debate/contested
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
Main Points Raised
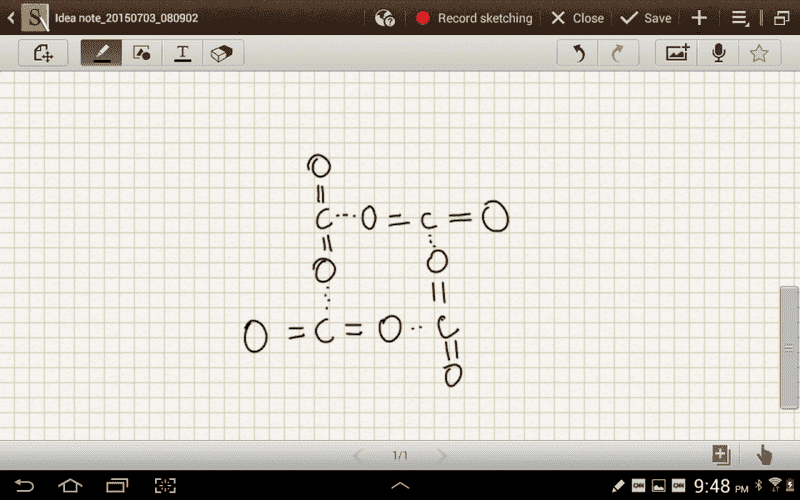
- Some participants note that CO2 has no net dipole moment due to its linear geometry, questioning why intermolecular forces from oxygen atoms of other CO2 molecules do not play a significant role.
- Others point out that while CO2 can exhibit arrangements in solid form, it is still characterized primarily by Van der Waals forces, leading to questions about the presence of dipole-dipole forces.
- A participant challenges the assertion that quadrupole-quadrupole interactions are negligible in CO2, suggesting that these forces may contribute to the intermolecular interactions.
- There is a discussion about the relative strengths of quadrupole interactions compared to London dispersion forces, with some participants suggesting that quadrupole forces could be stronger due to the higher electronegativity difference in CO2.
- Concerns are raised about the potential confusion between different types of van der Waals interactions, with a suggestion that the textbook may have oversimplified the discussion by only mentioning London dispersion forces.
- Participants express uncertainty about the quantitative comparison of quadrupole and dispersion forces, indicating that explicit calculations would be necessary to clarify their relative strengths.
- Some argue that while dispersion forces may be stronger overall, quadrupole forces still exist and could influence the properties of CO2.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants do not reach a consensus on the significance of quadrupole interactions in CO2 compared to London dispersion forces. Multiple competing views remain regarding the relative strengths and roles of these intermolecular forces.
Contextual Notes
Limitations include the complexity of estimating the magnitudes of quadrupole interactions and their comparison to dispersion forces, as well as the potential for differing interpretations of intermolecular forces in various contexts.
 .
.