You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Acceleration: Definition and 1000 Discussions
In mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time.
Accelerations are vector quantities (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the orientation of the net force acting on that object. The magnitude of an object's acceleration, as described by Newton's Second Law, is the combined effect of two causes:
the net balance of all external forces acting onto that object — magnitude is directly proportional to this net resulting force;
that object's mass, depending on the materials out of which it is made — magnitude is inversely proportional to the object's mass.The SI unit for acceleration is metre per second squared (m⋅s−2,
m
s
2
{\displaystyle {\tfrac {\operatorname {m} }{\operatorname {s} ^{2}}}}
).
For example, when a vehicle starts from a standstill (zero velocity, in an inertial frame of reference) and travels in a straight line at increasing speeds, it is accelerating in the direction of travel. If the vehicle turns, an acceleration occurs toward the new direction and changes its motion vector. The acceleration of the vehicle in its current direction of motion is called a linear (or tangential during circular motions) acceleration, the reaction to which the passengers on board experience as a force pushing them back into their seats. When changing direction, the effecting acceleration is called radial (or orthogonal during circular motions) acceleration, the reaction to which the passengers experience as a centrifugal force. If the speed of the vehicle decreases, this is an acceleration in the opposite direction and mathematically a negative, sometimes called deceleration, and passengers experience the reaction to deceleration as an inertial force pushing them forward. Such negative accelerations are often achieved by retrorocket burning in spacecraft. Both acceleration and deceleration are treated the same, they are both changes in velocity. Each of these accelerations (tangential, radial, deceleration) is felt by passengers until their relative (differential) velocity are neutralized in reference to the vehicle.
View More On Wikipedia.org
Accelerations are vector quantities (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the orientation of the net force acting on that object. The magnitude of an object's acceleration, as described by Newton's Second Law, is the combined effect of two causes:
the net balance of all external forces acting onto that object — magnitude is directly proportional to this net resulting force;
that object's mass, depending on the materials out of which it is made — magnitude is inversely proportional to the object's mass.The SI unit for acceleration is metre per second squared (m⋅s−2,
m
s
2
{\displaystyle {\tfrac {\operatorname {m} }{\operatorname {s} ^{2}}}}
).
For example, when a vehicle starts from a standstill (zero velocity, in an inertial frame of reference) and travels in a straight line at increasing speeds, it is accelerating in the direction of travel. If the vehicle turns, an acceleration occurs toward the new direction and changes its motion vector. The acceleration of the vehicle in its current direction of motion is called a linear (or tangential during circular motions) acceleration, the reaction to which the passengers on board experience as a force pushing them back into their seats. When changing direction, the effecting acceleration is called radial (or orthogonal during circular motions) acceleration, the reaction to which the passengers experience as a centrifugal force. If the speed of the vehicle decreases, this is an acceleration in the opposite direction and mathematically a negative, sometimes called deceleration, and passengers experience the reaction to deceleration as an inertial force pushing them forward. Such negative accelerations are often achieved by retrorocket burning in spacecraft. Both acceleration and deceleration are treated the same, they are both changes in velocity. Each of these accelerations (tangential, radial, deceleration) is felt by passengers until their relative (differential) velocity are neutralized in reference to the vehicle.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
S
Calculus Problem: acceleration, speed, and displacement of a particle
Homework Statement The acceleration of a particle given a=A√t where A=2.0 m/s5/2. At t=0, v=7.5 m/s and x=0. (a) What is the speed as a function of time? (b) What is the displacement as a function of time? (c) What are the acceleration, speed, and displacement at t=5.0s. Homework EquationsThe...- Stephanievet54
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Tangential acceleration and centripetal acceleration
a disc or radius r = 16cm starts spinning from rest with a uniform angular acceleration of 8.0 rad/s^2. at what time is its tangential acceleration twice the centripetal acceleration. i figured out the tangential acceleration is: Atan = α/R = 8 / .16 = 50 m/s^2 and the centripetal...- siapola1
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
N
Calculus angular acceleration with respect to theta
Homework Statement A disk with a 0.4 m radius starts from rest and is given an angular acceleration α = (10θ2/3)rad/s2 , where θ is in radians. Determine the magnitude of the normal (centripetal and tangential components of a point P on the rim of the disk when t = 4s. Homework Equations α =...- nick76342
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Thrust 6.05MN, mass 4,520,000 lbm, what is the acceleration?
if the first stage provides a thrust of 6.05 mega-Newtons [MN] and the space shuttle has a mass of 4,520,000 pound-mass [lb Subscript m], what is the acceleration of the spacecraft in miles per hour squared [mi divided by h squared]? Equation: F=ma conversions: 1000m=0.621mi 3600s=1 hour I'm...- dani546237
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
Why Does Acceleration Decrease When Velocity Increases in SHM?
When a mass is in SHM, and is moving towards equilibrium point, its velocity starts to increase but why does acceleration decreases? What is the gradient when velocity is increasing and when it is at maximum? Thanks a lot!- Josielle Abdilla
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration decrease Shm Velocity
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Mechanics
-
J
Instantaneous acceleration from Velocity-time graph
Homework Statement https://imgur.com/a/bvcxjNy Homework Equations Since the elevator is accelerating upwards, N - mg = ma or N = m(g+a) ------------ (1) The Attempt at a Solution In order to get the accelerations at that instant, I drew a tangent at that point and used v2 - v1/t2 - t1 = a...- James2911
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Why does radial acceleration act toward the center?
Acceleration of a rotating link has two components,Tangential (change in the direction) Radial (change in the magnitude). Why the direction of Radial acceleration is considered towards center (Centripetal)? what about centrifugal?- Athi Sankar
- Thread
- Replies: 21
- Forum: Mechanics
-

I Calculating Acceleration of Gravity w/ Geodesic Deviation: Troubleshooting
I have tried twice now to calculate acceleration of gravity using the general relativistic equation of geodesic deviation and both times my solution is twice the correct answer. What am I doing wrong? As an example here is one problem: Calculate the acceleration of gravity g at the earth’s...- Jim Hasty
- Thread
- Replies: 22
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Projectile motion problems with No horizontal acceleration
For projectile motion problems, we say that the horizontal component of the ball's path has no acceleration. The vertical component does, which is due to gravity, but in projectile motion it is true that horizontal and vertical motion are independent of each other. My question is in regards to... -
T
Objects approaching one another with uniform acceleration
Homework Statement persons 1 & 2 are initially at rest (vi=0m/s) 48m (d) apart. they then run towards each other at constant accelerations person 1 acceleration = 0.50m/s2 person 2 acceleration = 0.30m/s2 how long until they reach each other/collide (t)? at the instant they collide, how far...- ThatGuyNick
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Inertial force acceleration (vertical axis)
Hi, How is the inertial force Fi (acceleration) when the system is vertical. I noted Fi_horizontal=m.a, Ff=mg.μ.cos(Θ) et Fg=mg.sin(Θ) .- Justin71
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-
K
I Acceleration Frame Dependency - General Relativity
I was thinking about the geodesics equations and I realized that a particle will not have acceleration if the connection coefficients vanish, which (I think) is to say we are attatching a inertial frame to the particle. But if we attach a non-inertial frame to the particle, it will probably have...- kent davidge
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
Q
Electron in constant acceleration
If I throw the electron from electron gun with some acceleration .Will it maintain it's constant acceleration? If yes then it radiates photons from where will the electron gets energy to constantly radiate photon? If not then why?- Quantum9999
- Thread
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
A
I Calculating Velocity of a Ball in a Black Hole's Sphere of Influence
Warning: I'm a freshman chemistry student. My math skills are elementary at best. Image a ball in deep space. A baseball sounds nice. Assume this ball had no initial velocity but suddenly finds itself caught in the sphere of influence of a massive body. A black hole sounds fun. The ball begins...- alexchamp29
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Gravity
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
J
Calculate the acceleration of each mass at the instant the thread snaps
Homework Statement A piece of lead of mass 1.5 kg is suspended from a light spring. A copper sphere of mass 2.5 kg is suspended by keans of a thread as attatched to the lead. The thread is then burnt. Calculate the acceleration of each mass at the instant the thread snaps Homework Equations...- Josielle Abdilla
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Mass Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
H
Effect of time on the acceleration of an object initially at rest?
Hello, I recently bought a Dyson vacuum and have been excitedly vacuuming my floors way more than I need to! I have been doing some thinking as well on the matter (yes, vacuuming) and have a physics problem/question. It has been a long time since I studied physics, so I am not equipped to...- howsockgothap
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Inertia Rest Time
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Mechanics
-

I Colliding black holes: when will linear acceleration end?
I was musing about black hole mergers and what an observer might see for a particularly simple (i.e. blatantly contrived) scenario. Suppose that there are two (non rotating, un-charged, bog standard) black holes of dissimilar masses heading for a head-on collision. They will accelerate towards...- gneill
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
M
Requesting help with centripetal acceleration homework
Homework Statement A hockey puck of mass m = 80 g is attached to a string that passes through a hole in the center of a table, as shown in the figure below. The hockey puck moves in a circle of radius r = 1.10 m. Tied to the other end of the string, and hanging vertically beneath the table, is...- Myani
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Acceleration of mass depends upon K and L of a spring?
I have a question that appears elementary, but bizarre in its conclusion: A mass ##M## is accelerated by a spring of length ##L##, wave-speed ##v_p##, spring-constant ##K## and a constant force ##F## at the other end. As ##K## increases, the extension of the spring ##dx## decreases as does the...- John McAndrew
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Mechanics
-
C
Tension force and acceleration Problem
Homework Statement A block on an inclined surface is connected to another block that is hanging over the top edge of the incline, (as shown in the attached diagram). The system is moving in such a way that block B (mass = 3.0kg) is moving downwards, as block A slides up the ramp. The...- chef99
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
I
Does greater acceleration result in more work done?
Work W done by moving the object with force F for distance s is W = Fs. When I move the same object the same distance but with twice the acceleration, does the work done gets also doubled? By F=ma, doubling the acceleration yields m*2*a = 2F -> 2Fs = 2W. I've mostly read, that if I want to...- Imperial Sky
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Force Work Work done
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Mechanics
-
C
Circular Constant Acceleration Formula
A constant tangential force of magnitude 12N is applied to the rim of a stationary, uniform circular flywheel of mass 100kg and radius 0.5m. Find the speed at which the flywheel is rotating after it has completed 25 revolutions? I know that this can be done using work-energy. But since a...- CyclicCircle
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
I Acceleration vs Gravity in General Relativity
Hi, It is usually claimed that a person in an accelerating elevator with an acceleration equals to the gravity of the earth; this person cannot make any experiment that makes him know whether he is in the elevator or on the surface of earth. However, if this person project two light beams...- bgq
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
M
B Special Relativity & Acceleration: Unequal Inertial Frames
Given that one or both inertial frames must have been subject to acceleration at some point; resulting in an imbalance of application between the two inertial frames, why does the consequential effect of general relativity not feature in calculations. Surely, as such, neither observer's...- Martyn Arthur
- Thread
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
D
Acceleration forces acting on an elliptical mirror
Hi all, I need to bond the back surface of an elliptical mirror (75mm major diameter and 37.5mm minor diameter) onto a voice-coil actuated mirror mount that is going to be operating at 500 Hz and has an adjustment range of +-1.5 degrees. I need to determine the g-force likely to be acting on...- Doc
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Forces Mirror
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-
J
Acceleration of a particle on a parabola
Homework Statement A particle moves along a parabola on the x-y plane with equation ##y^{2}=2px## with constant speed ##1000m/s##.What is the magnitude of its acceleration? Homework Equations Parametric equations ##\vec{r}=(b^{2}t^{2}/(2p),bt)##. The Attempt at a Solution...- Jenny Physics
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-

How do you find the magnitude of acceleration?
Homework Statement . If F = 4.0 N and m = 2.0 kg, what is the magnitude a of the acceleration for the block shown below? The surface is frictionless. Homework Equations F=MA +/- Mg The Attempt at a Solution 19.6[/B]- mikelison womack
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Magnitude
- Replies: 24
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

How to find the aceleración and the rope forcé Fs?
<< Note -- formatting fixed up by a Mentor >> 1. Homework Statement Please see the attached image for the problem statement. Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution [/B] I uses the formula Fs = Fg1 +Fg2 + Ft1 + Ft2 I asumed the acceleration is equal to (F1+F2)/ m (4,9+19,6)/3 = 4,9ms^-2...- neon495
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Force Rope
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Speed of ball vs Acceleration of the ball?
Homework Statement Homework Equations v = s/t a = v/t The Attempt at a Solution My thinking was that through this small distance of air since velocity would increase due to the change in position changing at an increasing rate and thus since velocity is increasing then obviously...- Aaryan34532
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Ball Speed
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Question: How do I determine instantaneous acceleration using given data points?
Homework Statement A. Calculating instantaneous acceleration using formula: 1. According to ‘Table II’ data below: i. t=5 ii. t=15 iii. t=25 iv. t=35 v. t=45 Homework Equations The Attempt at a...- james digel
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
A
Acceleration on an inclined plane
Homework Statement The question says "A block of mass 4kg on a friction less inclined plane at angle of 30° is connected by a cord over massless friction less pulley to a second block of mass 2.3kg hanging vertically. What is the magnitude of acceleration of each block." Given m1 = 4 kg m2 =...- ANGLA
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
I Chain Rule and acceleration as a function of two variables
Hello Forum, When the force ##F## and its resulting acceleration ##a## have the most general form, the acceleration can depend on the position ##x##, time ##t## and speed ##v##. Newton's second law is given by ## \frac {d^2x}{d^2t}= a(x,t,v)##. When the acceleration is only a function of...- fog37
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Differential Equations
-
J
Is Hooke's law related to the time-squared rate of acceleration?
Is there a connection between the inverse square law of gravity and the time-squared rate that bodies fall (i.e. (32ft/second)/second))?- jbmolineux
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Gravity
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Mechanics
-
G
Radio Frequency Acceleration in Particle Accelerators
So, I've been really interested in Particle Physics since 6th grade when I did a project on particle accelerators. I understand most of it, except for one thing, the radio frequency cavities which are used for acceleration. I just want to ask, how do the Superconducting Radio Frequency Cavities...- General Scientist
- Thread
- Replies: 41
- Forum: Mechanics
-
J
Rank the four objects from fastest to slowest
Homework Statement Rank the four objects (1kg solid sphere, 1kg hollow sphere, 2kg solid sphere and 1kg hoop) from fastest down the ramp to slowest. (Please see the attached screenshot for more details.) Homework Equations KE_rot = 1/2Iw^2 (where omega = w) The Attempt at a Solution Since we...- JessicaHelena
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
L
Effective acceleration due to gravity in non-inertial frame
Take some sort of system accelerating with respect to an inertial reference frame: let's take a spherical mass on the end of a string forming a simple pendulum with the ceiling of a car, and allow that car to accelerate uniformly. Could someone share with me how they interpret the concept of a... -
F
The change in magnitude of centripetal acceleration
When an object (e.g. racecar) moves around in circles with constant tangential velocity, constant centripetal acceleration is present. What happens to the centripetal acceleration when the racecar is at rest, then increases its speed? I know that the tangential velocity increases due to the... -

Insights When Vehicle Power Dictates Acceleration - Comments
Greg Bernhardt submitted a new blog post When Vehicle Power Dictates Acceleration Continue reading the Original Blog Post.- jack action
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Power Torque Vehicle
- Replies: 34
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-
J
How to find the acceleration due to gravity inside a planet?
Consider a spherical planet of uniform density ρ. The distance from the planet's center to its surface (i.e., the planet's radius) is R. An object is located a distance R from the center of the planet, where R < Rp. (The object is located inside of the planet.) 1) Find an expression for the...- Johnnie123
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
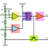
Given an acceleration figure calculate speed and distance
Homework Statement Serway Physics Chapter 2 19. A particle starts from rest and accelerates as shown in Figure P2.19. Determine (a) the particle's speed at t = 10.0s and at t = 20.0s and (b) the distance traveled in the first 20.0s Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution I am...- Alexanddros81
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Do I need to consider mass in the equations?
Homework Statement a. At launch a rocket ship has a mass M. When it is launched from rest, it takes a time interval t1 to reach speed v1; at t = t2, its speed is v2. What is the average acceleration of the rocket (i) from the start to t1 and (ii) between t1 and t2? For now, I am taking...- SavannahN
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Mechanics problem with two masses, a pulley and friction
Can anyone please explain to me how can I calculate the "Tension" and "acceleration" of M in this question interms of M,m1,m2 and g? I can't understand how M has an acceleration or why M is involved in the calculation of the tension my solution was that acc of M is zero and Tension = m1g x...- Ahmed Ayman
- Thread
- Replies: 23
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

A How Long To 'FreeFall' Into TON 618 From ISCO
So I'm trying to help someone get an idea of the 'scale' of some of the most massive black holes, but, I'm at best a laymen when it comes to this stuff. Because ISCO for a non-rotating black hole is just 3 times it's radius, and I can calculate apparent arc radius from ISCO, I could tell them...- Daharen
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
M
Transverse acceleration in polar coordinates
Homework Statement [/B] A particle is moving along a curve described by ##p(t) = Re^{\omega t}## and ##\varphi (t) = \omega t##. What is the particles transverse acceleration? Homework Equations [/B] None The Attempt at a Solution [/B] The position vector is ##Re^{\omega t} \vec{e_p}##...- marksyncm
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Calculating tensions and acceleration
Homework Statement A mass M1 is sliding across a table with coefficient of kinetic friction μk. A string is tied to this mass and runs over a pulley, drops vertically and is tied to another mass M2 which is falling. The pulley is connected to the table by a support. The pulley is a solid...- shepherd882
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
H
Maximum speed and magnitude of the acceleration of a spring?
Homework Statement If a midpoint of a guitar string executes simple harmonic motion following the form x(t)=Asin(wt+φ), and its angular frequency is ω = 2.76 × 103 s−1 and A=1.60mm. What is then its maximum speed of the string during this motion? And what is the maximum magnitude of the...- Howard Fox
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Acceleration of a car and jet plane problem
As we know, POWER is what accelerate a car, FORCE itself doesn't accelerate a car, if FORCE cousing movement it change into work, and work over time = POWER. The FORCE from jet engine pushes a plane forward. But as we know (or I'am wrong) FORCE don't push enything, only POWER couses...- vysqn
- Thread
- Replies: 89
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-
M
Direction of acceleration of an incline
Object with mass ##m## is sliding down a sloped (incline = ##\alpha##) object of mass ##M##. The coefficient of kinetic friction acting between ##m## and ##M## is ##\mu##. There is no friction between object ##M## and the ground. In the drawing above, the red vectors above are the forces acting...- marksyncm
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Direction Incline
- Replies: 24
- Forum: Mechanics
-

Use the data to construct a graph etc.
Homework Statement Serway Physics Section 2.4 Acceleration (a) Use the data in Problem 5 to construct a smooth graph of position versus time. (b) By constructing tangents to the x(t) curve, find the instantaneous velocity of the car at several instants. (c) Plot the instantaneous velocity...- Alexanddros81
- Thread
- Replies: 23
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Given a graph find aceleration
Homework Statement Serway Physics Section 2.4 Acceleration 17. Figure P2.17 shows a graph of ##v_x## versus t for the motion of a motorcyclist as he starts from rest and moves along the road in a straight line. (a) Find the average acceleration for the time interval t = 0 to t = 6.00 s. (b)...- Alexanddros81
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help