You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Black holes: Definition and 1000 Discussions
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing—no particles or even electromagnetic radiation such as light—can escape from it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can deform spacetime to form a black hole. The boundary of no escape is called the event horizon. Although it has an enormous effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, according to general relativity it has no locally detectable features. In many ways, a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light. Moreover, quantum field theory in curved spacetime predicts that event horizons emit Hawking radiation, with the same spectrum as a black body of a temperature inversely proportional to its mass. This temperature is on the order of billionths of a kelvin for black holes of stellar mass, making it essentially impossible to observe directly.
Objects whose gravitational fields are too strong for light to escape were first considered in the 18th century by John Michell and Pierre-Simon Laplace. The first modern solution of general relativity that would characterize a black hole was found by Karl Schwarzschild in 1916, and its interpretation as a region of space from which nothing can escape was first published by David Finkelstein in 1958. Black holes were long considered a mathematical curiosity; it was not until the 1960s that theoretical work showed they were a generic prediction of general relativity. The discovery of neutron stars by Jocelyn Bell Burnell in 1967 sparked interest in gravitationally collapsed compact objects as a possible astrophysical reality. The first black hole known as such was Cygnus X-1, identified by several researchers independently in 1971.Black holes of stellar mass form when very massive stars collapse at the end of their life cycle. After a black hole has formed, it can continue to grow by absorbing mass from its surroundings. By absorbing other stars and merging with other black holes, supermassive black holes of millions of solar masses (M☉) may form. There is consensus that supermassive black holes exist in the centers of most galaxies.
The presence of a black hole can be inferred through its interaction with other matter and with electromagnetic radiation such as visible light. Matter that falls onto a black hole can form an external accretion disk heated by friction, forming quasars, some of the brightest objects in the universe. Stars passing too close to a supermassive black hole can be shred into streamers that shine very brightly before being "swallowed." If there are other stars orbiting a black hole, their orbits can be used to determine the black hole's mass and location. Such observations can be used to exclude possible alternatives such as neutron stars. In this way, astronomers have identified numerous stellar black hole candidates in binary systems, and established that the radio source known as Sagittarius A*, at the core of the Milky Way galaxy, contains a supermassive black hole of about 4.3 million solar masses.
On 11 February 2016, the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo collaboration announced the first direct detection of gravitational waves, which also represented the first observation of a black hole merger. As of December 2018, eleven gravitational wave events have been observed that originated from ten merging black holes (along with one binary neutron star merger). On 10 April 2019, the first direct image of a black hole and its vicinity was published, following observations made by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) in 2017 of the supermassive black hole in Messier 87's galactic centre. In March 2021, the EHT Collaboration presented, for the first time, a polarized-based image of the black hole which may help better reveal the forces giving rise to quasars.
As of 2021, the nearest known body thought to be a black hole is around 1500 light-years away (see List of nearest black holes). Though only a couple dozen black holes have been found so far in the Milky Way, there are thought to be hundreds of millions, most of which are solitary and do not cause emission of radiation, so would only be detectable by gravitational lensing.
View More On Wikipedia.org
Objects whose gravitational fields are too strong for light to escape were first considered in the 18th century by John Michell and Pierre-Simon Laplace. The first modern solution of general relativity that would characterize a black hole was found by Karl Schwarzschild in 1916, and its interpretation as a region of space from which nothing can escape was first published by David Finkelstein in 1958. Black holes were long considered a mathematical curiosity; it was not until the 1960s that theoretical work showed they were a generic prediction of general relativity. The discovery of neutron stars by Jocelyn Bell Burnell in 1967 sparked interest in gravitationally collapsed compact objects as a possible astrophysical reality. The first black hole known as such was Cygnus X-1, identified by several researchers independently in 1971.Black holes of stellar mass form when very massive stars collapse at the end of their life cycle. After a black hole has formed, it can continue to grow by absorbing mass from its surroundings. By absorbing other stars and merging with other black holes, supermassive black holes of millions of solar masses (M☉) may form. There is consensus that supermassive black holes exist in the centers of most galaxies.
The presence of a black hole can be inferred through its interaction with other matter and with electromagnetic radiation such as visible light. Matter that falls onto a black hole can form an external accretion disk heated by friction, forming quasars, some of the brightest objects in the universe. Stars passing too close to a supermassive black hole can be shred into streamers that shine very brightly before being "swallowed." If there are other stars orbiting a black hole, their orbits can be used to determine the black hole's mass and location. Such observations can be used to exclude possible alternatives such as neutron stars. In this way, astronomers have identified numerous stellar black hole candidates in binary systems, and established that the radio source known as Sagittarius A*, at the core of the Milky Way galaxy, contains a supermassive black hole of about 4.3 million solar masses.
On 11 February 2016, the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo collaboration announced the first direct detection of gravitational waves, which also represented the first observation of a black hole merger. As of December 2018, eleven gravitational wave events have been observed that originated from ten merging black holes (along with one binary neutron star merger). On 10 April 2019, the first direct image of a black hole and its vicinity was published, following observations made by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) in 2017 of the supermassive black hole in Messier 87's galactic centre. In March 2021, the EHT Collaboration presented, for the first time, a polarized-based image of the black hole which may help better reveal the forces giving rise to quasars.
As of 2021, the nearest known body thought to be a black hole is around 1500 light-years away (see List of nearest black holes). Though only a couple dozen black holes have been found so far in the Milky Way, there are thought to be hundreds of millions, most of which are solitary and do not cause emission of radiation, so would only be detectable by gravitational lensing.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
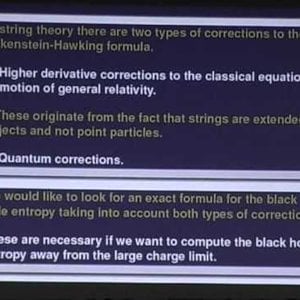
Extremal Black Holes in String Theory (1) by Ashoke Sen
Speaker : Ashoke Sen ( Harish- Chandra Research Institute, Allahabad, India ) Date and Time : 10 Aug 2009, 04:00 PM Venue : AG 66, TIFR, Mumbai In these lect...- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- black holes string theory
- Comments: 0
- Category: Beyond the Standard Model
-

Extremal Black Holes in String Theory (2) by Ashoke Sen
Speaker : Ashoke Sen ( Harish- Chandra Research Institute, Allahabad, India ) Date and Time : 11 Aug 2009, 04:00 PM Venue : AG 66, TIFR, Mumbai In these lect...- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- black holes string theory
- Comments: 0
- Category: Beyond the Standard Model
-

Extremal Black Holes in String Theory (3) by Ashoke Sen
Speaker : Ashoke Sen ( Harish- Chandra Research Institute, Allahabad, India ) Date and Time : 12 Aug 2009, 04:00 PM Venue : AG 66, TIFR, Mumbai In these lect...- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- black holes string theory
- Comments: 0
- Category: Beyond the Standard Model
-

I What problems would 'black holes' not being formed solve?
So when a star collapses, if the event horizon doesn't form, but the object remains in ordinary space, in increasing gravitational time-dilated collapse, what problems with these objects would be solved or more easily addressed? I would think at least the information loss problem, and then there...- DarkStar42
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes
- Replies: 90
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
H
Quantum Exploring Quantum Mechanics: ER=EPR, Black Holes, Firewalls & More
ER=EPR, black hole complementary, firewalls, vacuum entanglement etc.. Where do I begin studying these new ideas? I have a solid understanding about Quantum Field Theory and the classical theory of gravity, but no knowledge of string theory. Are there some advice or book recommendations anyone...- Higgsono
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Science and Math Textbooks
-
F
I Can an object be both a black hole and not a black hole?
According to Special Relativity, objects moving fast have more mass than objects at rest. So what if there is an object having a mass density near that required to create a black hole. Now if it were moving fast enough as well, it would gain enough mass density to become black hole. But to the...- friend
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes Relativity
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Black Holes: Draining Empty Spacetime?
If a black hole that is feeding is actually ingesting the spacetime around it (and hence whatever may lie in that spacetime including light) what does it do when it is not ingesting but nonetheless has very strong gravitational attraction? Does it sit there dragging empty spacetime into it? If...- Islam Hassan
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Empty Holes Spacetime
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
F
I Can Black Holes Transport Mass Back in Time?
According to Einstien's theory of evolution, the closer to the speed of light that an object travels, the slower it appears to move to an outside observer. (see https://www.thenakedscientists.com/forum/index.php?topic=40951.0) To take this to the next step once an object crosses the event...- FyrenEyce
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B How to shorten this speech about BH?
Hi guys I am writing a speech for a school video and I have a maximum of 3 minutes, but I've written 4 minutes and 17 seconds worth of stuff. I need help cutting the fat away giving me around 2 minutes and 45 seconds worth of stuff so that I can have some quick experiments and speak slower so...- avischiffman
- Thread
- Replies: 28
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

B Limitless Momentum of Black Holes
I am a hobby reader/listener of pysics, astronomy, special relativity, black holes and more. And a question arose that no amount of YouTube has touched on. Sorry if this is just a stupid question from a hobbist but it truly has me stumped. Or maybe I just have been taught by...- Sveinbjoern
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
B Thought Experiment from my daughter regarding black holes
My daughter is 12 and we like to discuss black holes. Here is our thought experiment: Gravity bends space and time lengthening both from the observers perspective. Does time slow down the farther you get from objects with density? Is there a place way way out, out of the range of the Big...- Mark Scalabrin
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Real-Life Demonstrations of Black Holes for Video
Hi, I am working on a video, and I was wondering if any of you knew of some real-life demonstrations I can do about black holes? So far I have the gravity well, and the balloon covered by foil that you crush to show same mass but denser. My video is about the anatomy of a black hole, so I cover...- avischiffman
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Black Hole Paradox: Exploring Gravity Waves
well since gravity waves are supposed to have mass, they are supposed to be effected by gravity itself, and :/ how are we supposed to detect gravitational waves emitted from a black hole when none can get out?- negative
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Do Black Holes Destroy Information?
Stephen Hawking proposed that black holes will eventually evaporate due to Hawking radiation, thus all information eaten by the black hole is destroyed. This violates basic physics, and hawking soon recanted his views, but there is still no real answer to whether they do or don't destroy...- TheQuestionGuy14
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes Information
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

A Gravitational binding energy and the TOV limit
Disclaimer: to avoid giving the impression of speculative nature, I state the purpose of this thread is only to conflate known theory with my own understanding in a specific point and clarify where the disagreement lies; that is all. TOV limit: since early research in black hole (BH) formation...- itssilva
- Thread
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
I Photon emission, power output (and black holes)
I recently re-read an article by Muller (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1606.07975.pdf) about the flow of time, and the possibility of time reversal given sufficient energy dissipation (basically during black hole evaporation, he concludes). Although the paper is on arXiv and not peer reviewed, Muller...- asimov42
- Thread
- Replies: 47
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

B Colliding black holes effect on the Richter scale
Would it make sense to ask? Is there any other scale for cosmic collisions? What about supernovae? Google is stupid sometimes.- jerromyjon
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes Scale
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-

I 10,000 black holes near Sagittarius A ?
Interesting sidebar in The Week (April 27, 2008, page 20) referencing a BBC.com news items (yeah, I know this is pretty indirect) that says a dozen binary pairs of black hole with orbiting stars have been identified near Sagittarius A by the Chandra X-ray Telescope. They go on to say and that...- phinds
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Cosmology
-

B What fraction of the matter in the universe is in black holes?
Conceptually, at least, this is a simple question, although I recognize that it might be hard to calculate in practice from available data. The matter-energy budget of the universe is measured (in a model dependent way) to consist of a certain percentage of dark energy, a certain percentage of... -
S
I Matter predominates b/c anti-matter fell into black holes?
I was reading an article about the great Steven Hawking, and it seems to say that matter & anti-matter can be created in space, but that one of them can fall into a black hole, thus leaving the other around in a higher preponderance, which of course matter is. So it would seem that a good...- swampwiz
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-

B Physicist who Questioned Black Holes
This is an article about the Indian physicist, Abhas Mitra, who questioned the theory of black holes and the loss of information long before Prof Hawking agreed that there is no Hawking radiation, no exact event boundary and no black hole information paradox...- jedishrfu
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes Physicist
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

I [Question] Tell me the latest catching news about black holes
Hello, Thank you for opening this thread. I am strongly interested in the universe, especially black hole. Though I am only eighteen years old, the more I read books about a black hole, the more my interest is getting powerful. Therefore, I want to know the latest and exciting news about...- BlackholeGirl
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
P
I Thermodynamics of Black Holes: Analyzing Carnot Cycles
Hello, I did read one paper about the Carnot cycle in a black hole. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1404.5982.pdf After formula (15) this paper says: 1) "The vanishing of CV is the “isochore equals adiabat” result, specific to static black holes, making our Carnot cycles particularly simple to make...- PeteSampras
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Is there a plan for a search for nearby black holes?
The thread https://www.physicsforums.com/threads/how-close-is-earth-to-the-closest-black-hole.939912/ reached a conclusion that there is a 65% confidence level that there is one black hole within 50 ly of Earth. The link http://www.solstation.com/stars/s20ly.htm says there are 25 stars bigger...- Buzz Bloom
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes Plan Search
- Replies: 55
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

B Light (not) escaping from black holes
Yet the neutron degeneracy pressure is unknown correct? Said size of neutron is a variable? What if we view the pressure as a volume knob, why could not a BH be viewed as a NS with the volume turned up from higher pressure?- Outhouse
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes Light
- Replies: 53
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
I Exploring the Effects of Dark Energy on Extremely Large Black Holes
Ordinarily a black hole’s Schwarzschild radius is linearly proportional to its mass. However, wouldn’t there be a deviation from this rule for extremely large black holes? Suppose we assume dark energy is due to a cosmological constant, whose value is the same everywhere (including inside the...- A Puzzlement
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

B Black Holes Must Have Singularities Says Einstein Relativity
https://www.forbes.com/sites/startswithabang/2018/02/14/black-holes-must-have-singularities-says-einsteins-relativity/amp/- Space_Girl
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Cosmology
-
P
B Photons, mass, and black holes
If photons are light particles, and they lack mass, how is it possible that they are affected by gravitational pull from a black hole? Super sorry if this has been asked / answered before, I couldn't find it on this forum if it has... Caveat No.2: My physics knowledge was limited to high school...- Philbert1893
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes Mass Photons
- Replies: 26
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Using Black Holes to Time Travel Into the Future
This is a possible science-fiction scenario, and I'm wondering if it is scientifically plausible. If someone wanted to take a one-way trip into future, say 1000 years from now, then SR gives you a possible way to do it without dying of old age: Just hop in a rocket ship, accelerate to nearly...- stevendaryl
- Thread
- Replies: 56
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
V
B Conflicting thought on quasars and black holes
After searching elsewhere online I could not find any information about this thought and hope someone may offer some insight. Black holes seem to be generally discussed as having a single entrance point from the event horizon and down into its singularity. I am confused by how quasars have...- VetStudent
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes Quasars
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
G
B Black holes and universe expansion
As we know the universe is expanding. Could this accelerating expansion contribute or cause black hole evaporation given that the strength of the gravitational force does not depend directly on time, while the distance of two given points in space increases with time? Sorry if my approach is... -
G
I Do Black Holes Have Walls? Exploring the Unknown
I was asked this question... Honestly I do not know! Imagine a black hole. You get sucked inside the singularity Yes, you'd die instantly, but suppose you lived. Where would you end up in space & time if, when inside the singularity, you float to a wall containing it and pierced it and traveled...- Gondur
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
B Are black holes infinitely dense?
If they are infinitely dense than, they would have infinite gravity, so if they have infinite gravity then the universe would have been sucked into a black hole. I was told that black hole has Infinite density so I want to clarify with you guys because it's logically didn't make sense to me.- Aliam1
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
D
I Is it possible to stretch a singularity?
Hi everyone When a smaller black hole gets sucked into a larger one, is it theoretically possible for the gravity of the larger black hole to stretch the smaller black hole so that it no longer has an infinitely dense centre? I guess it won't matter once they are completely merged, but in... -
F
A Primordial black holes need to be collisionless....
Primordial Black holes (PBH) need to be collisionless to be considered a serious Dark Matter candidate. Indeed a population of PBH with masses about 30 solar masses and uniformly distributed in the galaxy have very low capture and direct collision rates. But these PBHs should also behave as...- fhenryco
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Cosmology
-

B If Quark stars exist why do Neutron stars become Black holes?
From Wikipedia: Quark-degenerate matter may occur in the cores of neutron stars, depending on the equations of state of neutron-degenerate matter. It may also occur in hypothetical quark stars, formed by the collapse of objects above the Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff mass limit for...- wolram
- Thread
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

B Black Holes: Rotating vs Non-Rotating
I am reading about Kerr black holes and non rotating black holes. But I am unable to understand what decides whether the black hole will not rotate or rotate. And if No Hair theorem suggests, we can know about a black hole through its angular momentum, what implications does zero angular...- Souhardya Nandi
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes Rotating
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

A Why is all the mass of a BH in the singularity?
Hi everybody, and thanks in advance. My doubt is: why should the mass go in the singularity? I'm thinking about this situation: imagine a sphere with radius R<2M; then that sphere generates a BH. Schwarzschild tensor metric is valid only in the exterior region of the mass and for this reason i...- alex4lp
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Black Holes as Gateways to Parallel Universes?
I'd like to know people's views on the possibility of Black Holes being 'Gateways' or 'Portals' to parallel universes.- EnglandSP
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Can Black Holes Connect Lovers? Exploring Einstein-Rosen Bridges
I saw a video of a talk by Susskind discussing his ER = EPR idea. This post isn't actually about that talk, except that it got me thinking about wormholes. Without exotic means, I understand that it is basically impossible to have a traversible wormhole connecting two distant points in space...- stevendaryl
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Why is the time of formation of this Black Hole in question?
I have to 'question' the logic asked in the 'title question' asked in this artical: https://newatlas.com/most-distant-supermassive-black-hole/52508/?utm_source=Gizmag+Subscribers&utm_campaign=2151ebbb0d-UA-2235360-4&utm_medium=email&utm_term=0_65b67362bd-2151ebbb0d-91583997 It seems to me that...- SWB123
- Thread
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

I What happens if two black holes collide
I was reading up on the observation that occurred October of this year and started wondering what happens when two black holes collide do they merge to make one or do they collide as two separate objects kind of like two basketballs touching each other and also sort of a side question I've heard...- Dalton Peters
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
H
A Hawking radiation and rotating Black holes
Hawking radiation formula shows the fact that when charge and angular momentum increases in a Kerr-Newman black hole (angular momentum in Kerr black hole) Hawking radiation decreases. Can someone explain this? Thank you.- Hiranya Pasan
- Thread
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Do Black Holes Exist? Maths & Singularity Explained
Do Black Holes exist? after all the maths breaks down at the singularity Like the maths of the singularity breaks down at the beginning of the universe, what if there is no need for the maths to break down and these singularities do not exist?- wolram
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes
- Replies: 36
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

Exploring Black Holes, Second Edition
This is the updated version, free download- m4r35n357
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Science and Math Textbooks
-
A
I Where Did LIGO Find Merging Black Holes?
Surprisingly, I have not been able to find an answer to this question. How did scientists know where to build LIGO so that it would be able to find merging black holes in the sky? I assume LIGO is a permanent instrument so that it cannot be pointed to various parts of the sky, like an ordinary...- Albertgauss
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes Ligo
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Writing: Input Wanted Black holes here, white holes "on the other side"....
Beat this one up for me, please. I'm told it's an "against the mainstream" idea, so why that's true would be interesting to examine here. (Bear in mind I'm not an astrophysicist. That doesn't mean you can't post information that will leave me with a blank expression and a desire to find the...- Noisy Rhysling
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes
- Replies: 22
- Forum: Sci-Fi Writing and World Building
-
B Black holes in the centres of galaxies
Why is it believed that almost every big galaxy has a black hole on its center? Does the explanation rely on General Relativity?- davidge
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Galaxies Holes
- Replies: 27
- Forum: Cosmology
-
J
B Black holes cause neutron fusion in neutron stars
I read an article today stating that the possible explanation for the near total absence of heavier elements such as gold and uranium in many galaxies may be due to those galaxies not forming around a central black hole that has in absorbing one or more neutron stars causing fusion of neutrons...- JoeH
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
G
B Micro Black Holes: The Possibility of Creating an Extra Dimension
Would it be possible for an "extra" dimension to be created if a microscopic black hole was made and maintained until it sucked in a mass (a person) and was "turned on and off" infinitely quickly popping in and out of existence so that the gravity doesn't kill a human but the "extra dimension"...- Gilgamesh
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes Micro
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Special and General Relativity