You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Electromagnetism: Definition and 838 Discussions
Electromagnetism is a branch of physics involving the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force is carried by electromagnetic fields composed of electric fields and magnetic fields, and it is responsible for electromagnetic radiation such as light. It is one of the four fundamental interactions (commonly called forces) in nature, together with the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation. At high energy, the weak force and electromagnetic force are unified as a single electroweak force.
Electromagnetic phenomena are defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as different manifestations of the same phenomenon. The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. The electromagnetic attraction between atomic nuclei and their orbital electrons holds atoms together. Electromagnetic forces are responsible for the chemical bonds between atoms which create molecules, and intermolecular forces. The electromagnetic force governs all chemical processes, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms. Electromagnetism is very widely used in modern technology, and electromagnetic theory is the basis of electric power engineering and electronics including digital technology.
There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. Most prominently, Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.
The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, particularly the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the "medium" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.
View More On Wikipedia.org
Electromagnetic phenomena are defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as different manifestations of the same phenomenon. The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. The electromagnetic attraction between atomic nuclei and their orbital electrons holds atoms together. Electromagnetic forces are responsible for the chemical bonds between atoms which create molecules, and intermolecular forces. The electromagnetic force governs all chemical processes, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms. Electromagnetism is very widely used in modern technology, and electromagnetic theory is the basis of electric power engineering and electronics including digital technology.
There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. Most prominently, Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.
The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, particularly the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the "medium" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
Z
On which objects can we apply Gauss' Law to find the electric field?
What am I missing? I also don't get the title of the section: "Charge distributions with enough symmetry for Gauss's Law". I thought Gauss's Law was valid for any closed surface enclosing a charge. I don't understand what "enough symmetry" means in the title above. I get that with symmetry...- zenterix
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Z
Electric field is constant around charged infinite plane. Why?
Using Gauss's Law By using a symmetry argument, we expect the magnitude of the electric field to be constant on planes parallel to the non-conducting plane. We need to choose a Gaussian surface. A straightforward one is a cylinder, ie a "Gaussian pillbox". The charge enclosed is...- zenterix
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

What is the effect of a 1 cm gap on the magnetic field in a solenoid?
Hey, I was trying to figure out this problem. I got (a) using B = mu * NI/L but I'm not sure how to start the part about the magnetic field in the gap after the solenoid is ripped in half with 1 cm gap. Thanks for the help!- godiswatching_
- Thread
- Replies: 20
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-
Z
Calculate the electric field due to a charged disk (how to do the integration?)
I am interested in particular in the second integral, in the ##\hat{r}## direction. Here is my depiction of the problem: As far as I can tell, due to the symmetry of the problem, this integral should be zero. $$\int_0^R \frac{r^2}{(x^2+r^2)^{3/2}}dr\hat{r}$$ I don't believe I need to...- zenterix
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Z
Electric field created by two charged circular arcs?
The strategy will be to figure out what ##dq##, ##\hat{r}_{dq,p}##, and ##r_{dq,p}## are, plug them into the expression for ##d\vec{E}_{p_r}##, then integrate over ##d\vec{E}_{p_r}## to obtain ##\vec{E}_{p_r}##, the electric field at ##P## due to the arc on the right. Then I will repeat the...- zenterix
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Z
How to choose the correct function to use for a Taylor expansion?
Consider two different Taylor expansions. First, let ##f_1(s)=(1+s)^{1/2}## $$f_1'(s)=-\frac{1}{2(1+s^{3/2})}$$ Near ##s=0##, we have the first order Taylor expansion $$f_1(s) \approx 1 - \frac{s}{2}$$ Now consider a different choice for ##f(s)## $$f_2(s)=(1+s^2)^{1/2}$$...- zenterix
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Z
MIT OCW 8.02 Electromagnetism: how were these two limits calculated?
I know what the answers are, because this is all part of the notes from MIT OCW's 8.02 Electromagnetism course. In case you want to see the actual problem, it is example 2.3 that starts on page 18; the limits I am asking about are on page 20. How do I go about calculating the limits? Ie, what...- zenterix
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Electromagnetism Limits Mit ocw
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I How do photons transfer energy?
Hi! So I know about the electron-photon interaction but what about photon-photon interaction? I mean, I do know there is a very small chance for them to interact, but how else do they transfer energy in order to get from Sun to Earth, for example? When it comes to sound waves I get it, for...- Andreea007
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
K
I Gauge in the Aharonov Bohm effect
In p.385 of Griffiths QM the vector potential ##\textbf{A} = \frac{\Phi}{2\pi r}\hat{\phi}## is chosen for the region outside a long solenoid. However, couldn't we also have chosen a vector potential that is a multiple of this, namely ##\textbf{A} = \alpha \frac{\Phi}{2\pi r} \hat{\phi}## where...- KDPhysics
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
A
I Electron two-slit experiment in classical electromagnetism
Was there any study of this experiment in the context of classical electromagnetism? It is often claimed that such an experiment is impossible to explain classically, yet, the only classical model I've seen employed is Newtonian mechanics (bullets). The EM fields associated with the electrons...- AndreiB
- Thread
- Replies: 34
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

Classical Electromagnetism textbooks
I have always been interested in learning more about electromagnetism after going through Resnick Halliday Krane 5th edition. Upon reading a few ( read quite a lot) of E&M book threads, I have come to realize that the following texts are often pitched as alternatives to each other: Griffiths...- Falgun
- Thread
- Replies: 21
- Forum: Science and Math Textbooks
-
S
I How are the Maxwell's Electromagnetism equations traceless?
I was reading this:- swampwiz
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Electromagnetism
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
P
A Representing flux tubes as a pair of level surfaces in R^3
I am trying to see if Vector fields(I am thinking of electric and magnetic fields) without sources(divergence less) can be represented by a pair of functions f and g such that the level surfaces of the functions represent flux lines. I am trying to solve this problem in ## R^3 ## with a...- Prathyush
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Differential Geometry
-
M
I A problem when trying to compare electromagnetism with gravity
Let's say an object far far away from the Earth free falls in gravitational field. At Earth's surface free falling object gains kinetic energy E_1. Let's say an electron far away from the proton free falls in electromagnetic field. At Bohr's radius free falling electron gains kinetic energy E_2...- Myslius
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

I Origin of elecromagnetic field
Interesting thing, the undergraduate courses of electromagnetism states the electromagnetic field caused by electric charge: d∗F=4π/c∗J, and students, in my opinion, mistakenly imagine the electromagnetic field as a product of charged particle. In my opinion, it is more correct to say that...- sergiokapone
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Electromagnetism Field Origin
- Replies: 21
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-

B The resistance of an ohmic conductor
I know that the resistance of an ohmic conductor increases with length because the electrons going through the conductor must undergo more collisions in a longer conductor. But why decreasing the cross-sectional area of the conductor also increases the resistance of a conductor?- Viona
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
E
Electromagnetism and the movement of particles
- ellieee
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Is it Possible to Create a Large but Low-Powered Electromagnet?
Hi to everyone! I'm currently working on a University project and one of my crazy ideas needs me to get my hands on a pretty strange electromagnet. the measurements are 40cm by 40cm with a height of 3 to 5 cm (doesnt matter a lot) i don't need this magnet to be very powerful (just enough to...- MarcelloP
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
D
Can any object cause fluctuations in a magnetic field?
Summary:: Can a moving object cause disruptions in a magnetic field that could be detectable? Hello, I was hoping someone could assist me on a query I have regarding disruptions in a magnetic field. For some context, I am creating a science fiction story which features a non-humanoid alien...- Deleted member 690984
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Sci-Fi Writing and World Building
-

Lorentz force acting upon an electron moving in a circle
So as the summary suggests, I am studying Electromagnetism, magnetic properties of matter and Magnetization vector in particular. As a first example and to introduce the Magnetization vector (M), my textbook shows a ferromagnetic substance in a uniform magnetic field (B). Then, every atom of...- Ale_Rodo
- Thread
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

Electrostatic Potential Energy of a Sphere/Shell of Charge
So it seems the typical way to approach this problem is to consider the sphere when it has charge q and radius r. With uniform charge density ##\rho##, this becomes ##q = 4/3 \pi r^3 \rho## and so ##dq = 4 \pi r^2 dr \rho##. Using our expression for the potential outside of the sphere, we find...- sophiatev
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
U
Clarification on electric quadrupole moment definition
I have encountered two (?) definitions of the electric quadrupole moment. They are: $$Q_{ij}=\frac{1}{2}\int \rho(\vec{x}')x'_i x'_j\,\mathrm{d}^3x'$$ and $$Q_{ij}=\int (3x'_i x'_j-\delta_{ij}x'^2)\rho(\vec{x}')\,\mathrm{d}^3x'$$ I am trying to study radiation arising from the electric...- user1139
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

B How does a photon not "feel" electromagnetism?
I've attached a picture of a table in Sean Carroll's The Particle at the End of the Universe. It says that photons don't "feel" electromagnetism, but gluons feel the strong force, the W and Z bosons feel the weak force, and gravitons feel gravitation. How is this so? (I have no formal quantum...- Marshall2389
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Electromagnetism Photon
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
J
Electromagnetic inertial reaction force?
I accelerate charged particle ##A## causing virtual photons to travel to distant charged particle ##B## which feels an electromagnetic force proportional to ##A##'s acceleration (for a classical field description of this effect see https://www.feynmanlectures.caltech.edu/I_28.html Eqn 28.6)...- jcap
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
A
Electromagnetism - movement of a coil in a magnetic field
So my idea was that to reach the equilibrium position, the final moment of force has to be 0 (so in the end the forces will “eliminate” each other). And I found the equation Fm=B*I*l*sinα, which should characterize the force, which affects wire with the current in a magnetic field, and Fleming’s...- Ali123
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

I General relativity, Electromagnetism and Feynman Diagrams
We are discussing the introduction to Einstein field equation, so he start talk about the linearity in Newtonian gravity and the non linearity in GR. But there is somethings I am missing: > " (...) in GR the gravitational field couples to itself (...) A nice way to think about this is provided...- LCSphysicist
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
K
Classical Best undergraduate electromagnetics textbook
Hi I am looking for a textbook that covers most of the topics in a general undergraduate electromagnetics course. It would be great if the topics below are covered. I don't mind getting a few but would like to find a good explanation of these topics. thanks Gauge invariance Lorenz gauge Greens...- ksnaz12
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Science and Math Textbooks
-

A Is There a Unified Theory Between General Relativity and Electromagnetism?
I want know is there any unified and consistent theory between general relativity and electromagnetism ? If yes could you provide me any textbook ? I'm interest- Karimselim1997
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Electromagnetism Gravity
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Energy-Momentum Tensor for Electromagnetism in curved space
a) I'd separated the Lagrangian into: $$ \mathcal L = \mathcal L_{Max}+\mathcal L_{int} $$ in which ##\mathcal L_{Max} =\frac{-1}{4}\sqrt{-g} F^{\mu \nu}F_{\mu \nu}## and ##\mathcal L_{int} =\sqrt{-g} A_\mu J^\mu## Thus: $$ T^{\mu \nu}_{Max}= F^{\mu...- Pouramat
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
C
Electromagnetism and the Pauli Exclusion Principle
Electromagnetism in the atoms is why we can't pass through a bank vault. But supposed electromagnetism were canceled for an object, what would happen to the residual or remaining Pauli Exclusion principle? Would it still cause resistance to passing through the vault? On a second scenerio, what...- Cobul
- Thread
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
J
I Does Poynting's Theorem only involve external fields?
Poynting's Theorem (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Poynting's_theorem) says: The rate of energy transfer (per unit volume) from a region of space equals the rate of work done on a charge distribution plus the energy flux leaving that region. $$-\frac{\partial u}{\partial...- jcap
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

Question about this Continuity Equation (electromagnetism)
Hello All : reading the Bo Thide book in electromagnetism , downloaded the draft copy from the following link http://www.plasma.uu.se/ , i reached the chapter 4 now and a section in that chapter (section 4.3) have few lines that i coudnt understand (mathematically speaking) the writer conclude...- hagopbul
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
U
Derivation of torque on general current distribution
How do I simplify the expression...- user1139
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

Classical Relativistic Electromagnetism (Undergrad Level)
I have looked several special relativity books but in each of them the metric is defined as ##\eta_{\nu\mu} = (+1, -1, -1, -1)##. Is there a book where the metric is defined as ##\eta_{\nu\mu} = (-1, +1, +1, +1)## ?- Arman777
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Science and Math Textbooks
-
Find an expression for a magnetic field from a given electric field
Here this is my attempt : Reference Textbook : Zangwill's Modern Electrodynamics I stuck at the last step , I really have no idea what to do next.- TechieDork
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

Work done via induced charges in a grounded conductor
I'm currently studying Method of Images in Griffiths book and in section 3.2 he introduces the method of images for a point charge at a distance ##d## from a grounded conducting plane at potential ##V = 0##. In subsection 3.2.3, Griffiths compute the energy of the real system and the image...- GeniVasc
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
B
Electromagnetism -- What do charges have to do to create EM waves?
I am not sure, but I think the answer is between acceleration and velocity.- bbbbb
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
How to insulate an object with electromagnetism?
Hi. I've got two questions. Is it true that waves with longer wavelengths are handled easier? Think of a scenario where radio-waves insulate a solid object (in a lab for example). How can this be done? Given my understanding, waves don't travel around the environment uniformly.- Atran
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Electromagnetism
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
P
Interactions Between 2 Dipoles
Draw graphs showing how interaction energy depends upon the relative orientation of two dipoles if (i) p1 is parallel to r, (ii) p1 is perpendicular to r. I've done the first part and found the interaction energy as UInt = 1/(4*pi*epsilon0*r^3)*[p1.p2-3(p1.r^)(p2.r^)] which I know is correct...- physconomic
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

Electromagnetic Induction of a Disk
Hello I'm having trouble finding the right way to apply Faraday's law to this question. I've found the flux through the disc: ##\phi = \vec A \cdot \vec B = B_{0} \sin{\omega t} \left( \frac D 2 \right)^2 \pi ## and the EMF: ##\varepsilon = - \frac {d \phi} {dt} = -B_{0} \omega \cos{\omega t}...- Mr_Allod
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
R
Size of bremsstrahlung radiation fields generated by linear accelerators
Hi everyone, sorry we are talking about pulsed power accelerators again. In this context, it is about the HERMES III again. According to https://apps.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/a351472.pdf HERMES III, a 16 terawatt pulsed power accelerator at Sandia National Labs, which fired electron beams...- Rev. Cheeseman
- Thread
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Electrical Engineering
-

Electromagnetism: Determining Induced EMF
- Pi314227
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
Electric Potential inside an insulating sphere
I used the potential at the surface of the sphere for my reference point for computing the potential at a point r < R in the sphere. The potential at the surface of the sphere is ## V(R) = k \frac {Q} {R} ##. To find the potential inside the sphere, I used the Electric field inside of an...- baseballfan_ny
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
V
Find the potential using a line integral (Electromagnetism)
Sorry - I wish I had some way of writing equations in this forum so the "relevant equations" section is easier to read. The answer to the first part is (a) so the rest follows from using the electric field given in B. If anyone is interested this question comes from Griffith's 3rd edition...- Vitani1
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Electromagnetism: Force between two charged plates
Hello, I need to find the force between the two metal plates, one is charged positively, and another is charged negatively. I have to use surface integration, but then I get two surface integrations because of the two differently charged plates. Now I am confused. Please help me. Thank you in...- oondi
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Minimium diameter of an electromagnetic beam in terms of wavelength
Is there a limit on the minimum diameter that a collimated electromagnetic beam must have (lasers or masers), in terms of its wavelength, or it is possible to create a beam with its diameter smaller than its wavelength? I'm considering a colimated planar wave directly from the source, and not...- Uchida
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
F
Does the theory of electromagnetism have this fundamental problem?
This is about possible problems with the equations of EM theory of Faraday and Maxwell. EM theory states that when an electron moves a magnetic field is generated. Does this field move with electron in the direction of the electron (if the electron is in motion)? Or, does it stay still in the...- francis20520
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
J
I Falling EM system contradicts the equivalence principle?
The following is an improved version of my previous post https://www.physicsforums.com/threads/falling-electric-dipole-contradicts-the-equivalence-principle.964594/ Consider the following system comprising a particle on the left with charge ##+q## that is a large distance ##d## away from two...- jcap
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
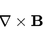
Magnetic field (correction term)
Ampere´'s law with the correction term I have a infinite cylinder with radius R with a current density , and magnetic field . I have to proof that it is acceptable to discard the correction term of term of ampere's law, while calculating the magnetic field, as long as it obeys the following...- anaisabel
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
K
E&M: Field of a Wire with non-uniform current
Summary:: Not sure if my solution to a magnetostatics problem is correct [Mentor Note -- thread moved from the technical forums, so no Homework Template is shown] I was trying to solve problem 2 from...- KDPhysics
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help