- #1
ChiralSuperfields
- 1,216
- 132
- Homework Statement
- Please see below
- Relevant Equations
- Please see below
For this,
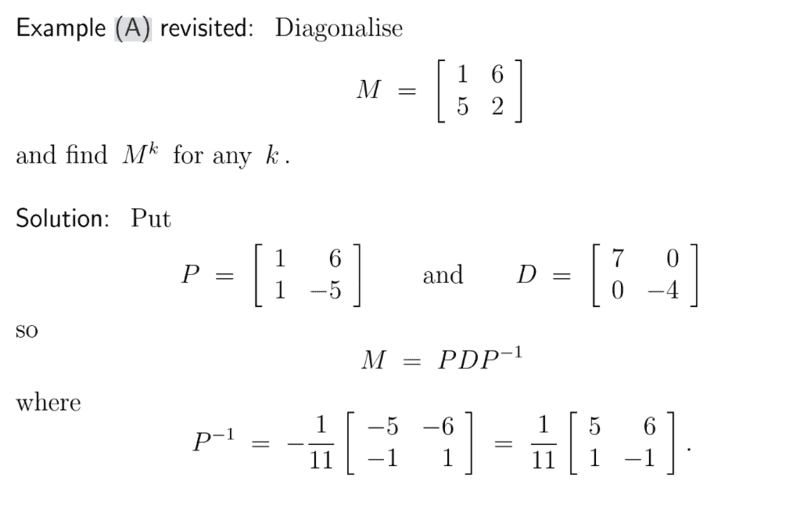
Dose someone please know where they get P and D from?
Also for ##M^k##, why did they only raise the the 2nd matrix to the power of k?
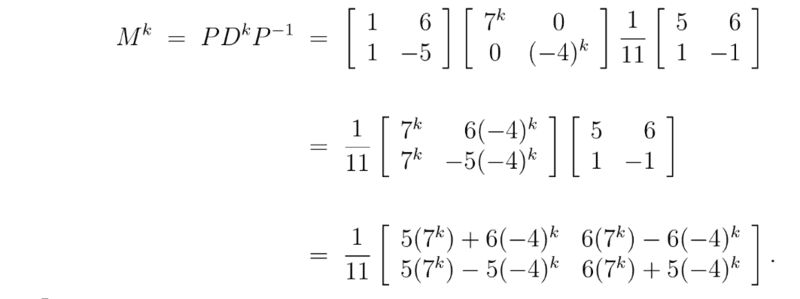
Many thanks!
Dose someone please know where they get P and D from?
Also for ##M^k##, why did they only raise the the 2nd matrix to the power of k?
Many thanks!