- #1
Clarky48
- 6
- 0
It's my first post so big thanks in advance :)
1. Homework Statement
So the question states "By interpreting <pxΨ|pxΨ> in terms of an integral over x, express <Ekin> in terms of an integral involving |∂Ψ/∂x|. Confirm explicitly that your answer cannot be negative in value." ##The 'px's should have hats to indicate an operator##
If it helps, it's part of a question where Ψ is the wavefunction of a particle in a 1D pot energy well and the question is testing on a chapter about introducing and working with Dirac notation.
None that I can think of
The maths of my solution so far is
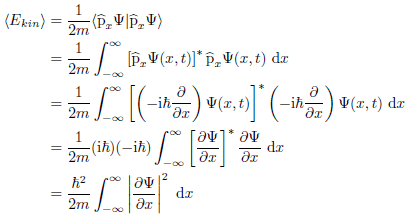
So, the part I'm stuck with is proving explicitly that it can't be negative in value. Obviously the factor to the left is always positive but it's the integral that's the problem. I know the integrand is always real and positive as it's a modulus squared, I just can't see any way to prove that the integral of that, over infinity, is never negative.
It's due in for next Monday so any help would be greatly appreciated!
1. Homework Statement
So the question states "By interpreting <pxΨ|pxΨ> in terms of an integral over x, express <Ekin> in terms of an integral involving |∂Ψ/∂x|. Confirm explicitly that your answer cannot be negative in value." ##The 'px's should have hats to indicate an operator##
If it helps, it's part of a question where Ψ is the wavefunction of a particle in a 1D pot energy well and the question is testing on a chapter about introducing and working with Dirac notation.
Homework Equations
None that I can think of
The Attempt at a Solution
The maths of my solution so far is
So, the part I'm stuck with is proving explicitly that it can't be negative in value. Obviously the factor to the left is always positive but it's the integral that's the problem. I know the integrand is always real and positive as it's a modulus squared, I just can't see any way to prove that the integral of that, over infinity, is never negative.
It's due in for next Monday so any help would be greatly appreciated!