- #1
Srv44
- 3
- 0
Hello all,
I am working on a dye doping project and got a photospectrometry result as show in a picture for my thin film. Can anyone please help me interpret the physical meaning of the graph below? Thanks!
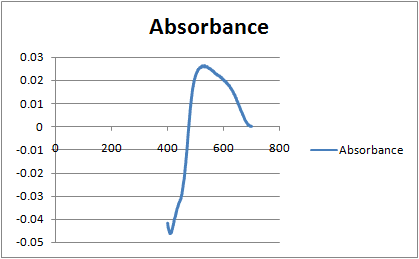
I am working on a dye doping project and got a photospectrometry result as show in a picture for my thin film. Can anyone please help me interpret the physical meaning of the graph below? Thanks!