yuiop
- 3,962
- 20
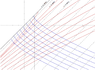
The attached diagram is a plot of two free falling observers (vertical black lines) in Lemaitre coordinates. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lemaitre_metric
The solid black diagonal line is the central singularity. Curved blue lines are ingoing light paths and curved red lines are outgoing light rays. The diagonal dashed grey lines are lines of constant radius in Schwarzschild coordinates.
The Wiki article gives some information on the Lemaitre metric but some additional information and calculations are need to obtain the equations in a form that can be plotted on a graph.
A curious feature highlighted by the diagram is that despite the distance between the two free falling observers being constant in terms of Lemaitre spatial coordinates, the radar distance is increasing in terms of the Lemaitre time coordinate which I assume is just the proper time of a falling observer. It is also clear from the diagram that far away from the gravitational source where spacetime becomes flat, the speed of light in Lemaitre coordinates does not tend towards c, but tends towards infinite.
The solid black diagonal line is the central singularity. Curved blue lines are ingoing light paths and curved red lines are outgoing light rays. The diagonal dashed grey lines are lines of constant radius in Schwarzschild coordinates.
The Wiki article gives some information on the Lemaitre metric but some additional information and calculations are need to obtain the equations in a form that can be plotted on a graph.
A curious feature highlighted by the diagram is that despite the distance between the two free falling observers being constant in terms of Lemaitre spatial coordinates, the radar distance is increasing in terms of the Lemaitre time coordinate which I assume is just the proper time of a falling observer. It is also clear from the diagram that far away from the gravitational source where spacetime becomes flat, the speed of light in Lemaitre coordinates does not tend towards c, but tends towards infinite.
Attachments
Last edited: