- #1
StripesUK
- 23
- 2
Homework Statement
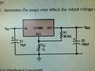
FIGURE 2 shows an adjustable voltage regulator using the LT1083
.The LT1083 develops a 1.25V reference voltage between the output and the
adjust terminal. By placing a resistor R1 between these two terminals, a constant
current is caused to flow through R1 and down through R2 to set the overall
output voltage.
If VIN=18V, determine the range over which the output voltage can be varied.
Homework Equations
[itex]V OUT=V REF*(1+ \frac{R2}{R1})[/itex]
The Attempt at a Solution
[itex]V OUT=1.25*(1+ \frac{1000}{90.9})=15V[/itex]
[itex]V OUT=1.25*(1+ \frac{0}{90.9})=1.25V[/itex]
The output voltage range being 1.25-15V
This is the only equation I can find relating to the output voltage of the regulator. By making two calulations using 0 and 1K ohms of R2 this would give me the range I am looking for, but what is confusing me is the fact that they have given me a V IN. Is this just a false trail or am I actually missing something?