- #1
jT990
- 1
- 0
Hello all,
I am after some advice regarding a hall sensor type air flow meter.
I know from experience that most hall sensor flow meters allow a bypass of fluid around the turbine/fan. However I would like to know what would happen if this was the case of the design below.
Specifications;
Inlet air velocity 0-11.5ms-1
Inlet ID 1.5mm
Turbine diameter: 5mm
Air gap between turbine and housing: 0.1mm
I assume two things will happen,
1.) the turbine itself will impede intake air velocity and eventually reach zero.
and/or 2.) the turbine will rotate too fast and the turbulence created inside the housing will in turn impede intake air.
I will attach calculations shortly.Thanks in advance.
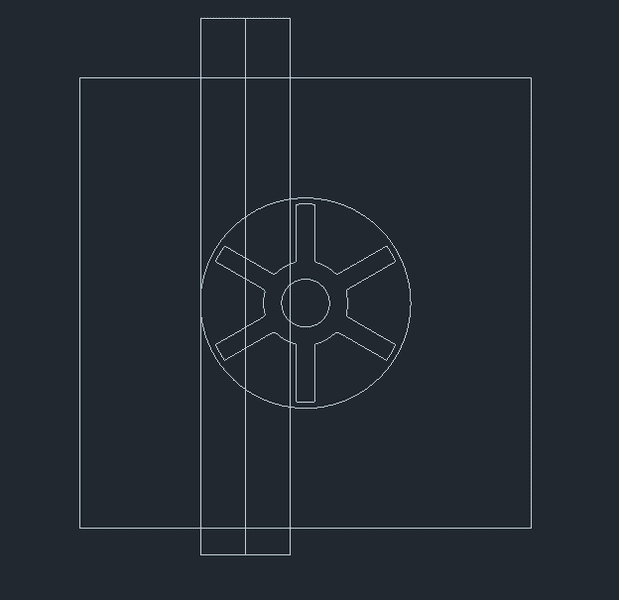
I am after some advice regarding a hall sensor type air flow meter.
I know from experience that most hall sensor flow meters allow a bypass of fluid around the turbine/fan. However I would like to know what would happen if this was the case of the design below.
Specifications;
Inlet air velocity 0-11.5ms-1
Inlet ID 1.5mm
Turbine diameter: 5mm
Air gap between turbine and housing: 0.1mm
I assume two things will happen,
1.) the turbine itself will impede intake air velocity and eventually reach zero.
and/or 2.) the turbine will rotate too fast and the turbulence created inside the housing will in turn impede intake air.
I will attach calculations shortly.Thanks in advance.
Attachments
Last edited: