karush
Gold Member
MHB
- 3,240
- 5
Rectangle ABCD is inscribed in the circle shown.
If the length of side $\overline{AB}$ is 5 and the length of side $\overline{BC}$ is 12
what is the area of the shaded region?
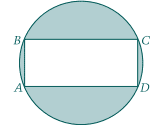
$a.\ 40.8\quad b.\ 53.1\quad c\ 72.7\quad d \ 78.5\quad e\ 81.7$
well to start with the common triangle of 12 5 13 gives us the diameter of 13
area of the circle is $\pi \left(\frac{13}{2}\right)^2=132.73$
area of {circle - retangle)=$132.73-60 =72.7$ which is c
typos maybe:unsure:
If the length of side $\overline{AB}$ is 5 and the length of side $\overline{BC}$ is 12
what is the area of the shaded region?
$a.\ 40.8\quad b.\ 53.1\quad c\ 72.7\quad d \ 78.5\quad e\ 81.7$
well to start with the common triangle of 12 5 13 gives us the diameter of 13
area of the circle is $\pi \left(\frac{13}{2}\right)^2=132.73$
area of {circle - retangle)=$132.73-60 =72.7$ which is c
typos maybe:unsure:
Last edited: