- #1
shauntur
- 3
- 0
Not Really a homework question but it will help with how i go about the homework.
So i have a beam coming out of the wall and it has force acting on it like this:
Woops, that 20 on the side view should be a 10 :P
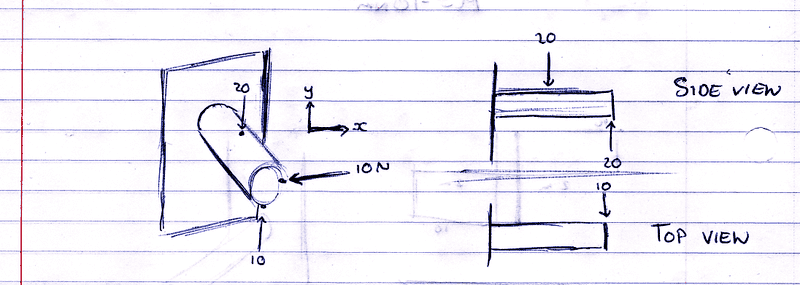
What i want to find is the total moment at the mid point. I know how to find the moment in each direction but I am not sure if I am aloud to add them together or use pythag??
heres my solution for each direction:
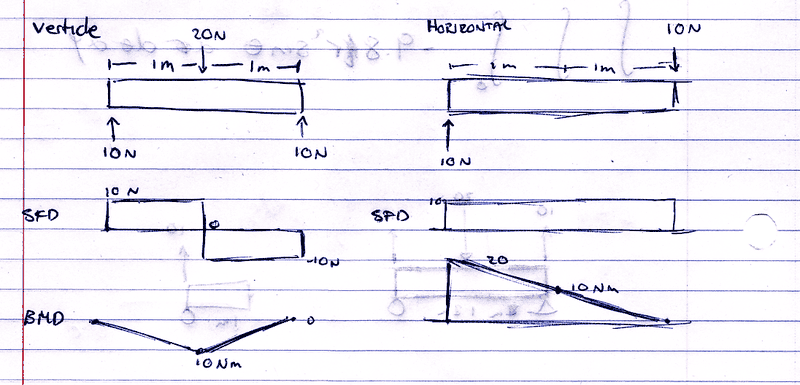
Can i just go sqrt(10^2+10^2) to give me 10?
Thanks
Shaun
So i have a beam coming out of the wall and it has force acting on it like this:
Woops, that 20 on the side view should be a 10 :P
What i want to find is the total moment at the mid point. I know how to find the moment in each direction but I am not sure if I am aloud to add them together or use pythag??
heres my solution for each direction:
Can i just go sqrt(10^2+10^2) to give me 10?
Thanks
Shaun