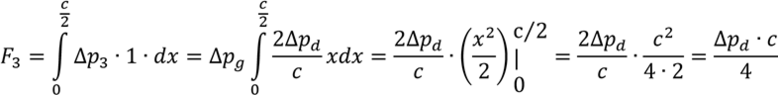Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the calculation of lift from pressure distribution on an airfoil, addressing theoretical and mathematical aspects of lift generation, pressure differentials, and the relevance of airfoil geometry. Participants explore how pressure distribution relates to lift and drag calculations, and the implications of surface orientation.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant presents a calculation for lift based on pressure differentials and expresses confusion about the orientation of forces acting on the airfoil surfaces.
- Another participant clarifies that the pressure discussed is a differential pressure, which can be negative, and questions the necessity of airfoil geometry for lift calculations if pressure distribution is known.
- Some participants argue that while the shape of the airfoil is relevant for creating pressure distribution, it may not be necessary for calculating lift if the pressure distribution is provided.
- There is a correction made regarding the need for pressure distribution, surface area, and surface orientation to accurately calculate forces.
- Participants discuss the concept of surface orientation, defining it as the direction of the normal vector at a point on the surface, which affects the force due to pressure.
- Questions arise about the calculation of forces based on pressure distribution, particularly regarding the treatment of pressure acting on the airfoil surfaces and the implications of surface angles.
- One participant suggests that pressure forces can be treated as acting vertically on a flat surface for simplification, while another points out the importance of understanding how pressure distribution changes with angle of attack.
- Resources are requested for further learning about lift calculations and pressure distribution.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the relevance of airfoil geometry in lift calculations, with some asserting it is unnecessary if pressure distribution is known, while others argue that geometry is essential. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the interpretation of pressure forces and their application in calculations.
Contextual Notes
There are limitations in the discussion regarding assumptions about surface angles and the treatment of pressure forces, which may affect the accuracy of lift calculations. The dependence on specific definitions of pressure and surface orientation is also noted.
Who May Find This Useful
This discussion may be useful for individuals interested in aerodynamics, fluid dynamics, and the mathematical modeling of lift and drag forces on airfoils.