SUMMARY
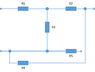
The discussion focuses on calculating the equivalent resistance between various terminals in a circuit involving resistors R1, R2, R3, and R4. The user initially attempted to calculate the resistance between terminals 1 and 2 using the formula (R1 + R2) || (R1 + R2 + R3) but expressed confusion regarding the identification of series and parallel resistors. Key insights include the importance of recognizing nodes in the circuit and the suggestion to redraw the circuit for clarity, particularly when considering the impact of a battery on the arrangement of resistors.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of series and parallel resistor configurations
- Familiarity with circuit nodes and equipotential lines
- Basic knowledge of Ohm's Law and voltage drops
- Ability to redraw circuits for clarity
NEXT STEPS
- Learn how to calculate equivalent resistance in complex circuits
- Study circuit analysis techniques using Kirchhoff's laws
- Explore the impact of adding a voltage source on resistor configurations
- Practice redrawing circuits to simplify analysis of series and parallel resistors
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, hobbyists working with circuits, and anyone needing to calculate equivalent resistances in complex resistor networks.