becka221
- 2
- 0
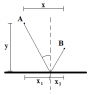
Im trying to calculate the refelction angle of 2 points in a 2d plane, but not the same distance away from the reflection surface, and I'm drawing a blank.
Any help would be hugely appreciated.
Any help would be hugely appreciated.