nobb
- 33
- 0
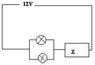
The identical lamps in the circuit (attachment) each have a resistance R at their rated voltage of 6V. The lamps are to be run in parallel with each other using a 12V source and a series resistor Z in the circuit as shown. If the lamps are to operate at their rated voltage, what must be the resistance of Z?
A. R/2
B. R
C. 2R
D. Zero
Any ideas?
A. R/2
B. R
C. 2R
D. Zero
Any ideas?