quanticism
- 29
- 3
Hi,
I'm confused at why cathodes are the positive terminal in chemistry but appear to be the negative terminal in physics. I hope someone can clear this up for me.
Definitions:
Anode: An anode is an electrode through which conventional current flows into a polarized electrical device.
Cathode: A cathode is an electrode through which conventional current flows out of a polarized electrical device
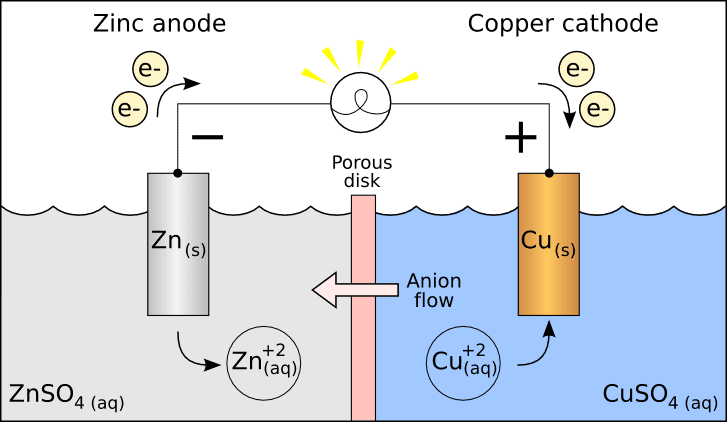
Galvanic Cell
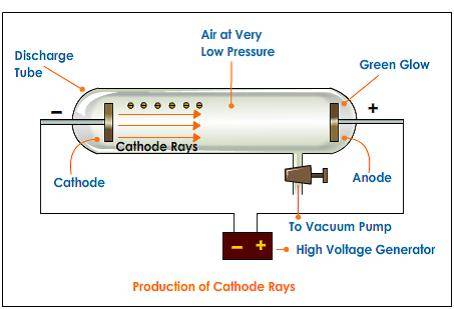
Vacuum Tube
Going by the definition above, I agree with the galvanic cell "cathode/anode" labels.
However, looking at the vacuum tube, the electrons traveling to the right through the partial vacuum and entering the anode, ie conventional current is leaving the anode which seems to contradict the provided definition.
I'm confused at why cathodes are the positive terminal in chemistry but appear to be the negative terminal in physics. I hope someone can clear this up for me.
Definitions:
Anode: An anode is an electrode through which conventional current flows into a polarized electrical device.
Cathode: A cathode is an electrode through which conventional current flows out of a polarized electrical device
Galvanic Cell
Vacuum Tube
Going by the definition above, I agree with the galvanic cell "cathode/anode" labels.
However, looking at the vacuum tube, the electrons traveling to the right through the partial vacuum and entering the anode, ie conventional current is leaving the anode which seems to contradict the provided definition.