- #1
oy_katet
- 3
- 0
Homework Statement
A neutron (mass 1.7x10-27 kg) traveling at 2.7 km/s hits a stationary lithium nucleus (mass 1.2x10-26 kg). Afterwards, the velocity of the lithium nucleus is 0.40 km/s at 54° to the original direction of the motion of the neutron. If the speed of the neutron after the collision is 2.5 km/s, in what direction is it traveling?
[Answer: 66° from initial direction of neutron's velocity]
Homework Equations
Givens:
m1= 1.7x10-27 kg
v1x= 2.7 km/s
v'1x= (2.5)cosθ
v'1y= -(2.5)sinθ
m2= 1.2x10-26 kg
v2x= 0 km/s
v'2x= (0.4)cos54°
v'2y= (0.4)sin54°
Equations:
m1v1x= m1v'1x+m2v'2x
0= m1v'1y+ m2v'2y
The Attempt at a Solution
I plugged in my values into the two equations, and for the first equation using the x-values I got θ= 65.42° and the second using the y-values I got 65.51°. I was wondering if anyone could point me in the right direction?
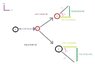
I've attached a diagram of my thought process.