dss975599
- 31
- 1
Homework Statement
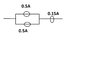
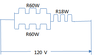
One 18 watt lamp and two 60-watt light bulb are plugged into a 120V circuit. For either DC or AC, the two bulbs are connected each other in parallel and in series with the lamp in the same circuit. Calculate;
i. the current flow through each light
ii. the total resistance of the circuit,
The soultion provided is I1 = P /V = 18 /120 = 0.15A ,
I2 = P / V = 60/120 = 0.5A
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
I have tried to sketch the diagram as attached .
R1= 120/ 0.15 = 800 ohm , R2 = 120/0.5 = 240 ohm
I doubt the ans is correct . When i check thru the working again , i found that the V total = 0.15(800) + 0.5(240) = 240V ...
So , i think it's wrong ...
Correct me if i am wrong
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: