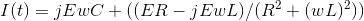Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around calculating the complex current in a parallel R-L circuit, specifically focusing on the contributions from a resistor, inductor, and capacitor. Participants are exploring the application of Ohm's law and impedance in the context of AC circuit analysis, with an emphasis on expressing the current in terms of complex numbers.
Discussion Character
- Homework-related
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- Some participants express uncertainty about the correct approach to find the complex current, with references to using Ohm's law and total impedance calculations.
- There is a discussion about the configuration of the circuit, with some clarifying that the resistor and inductor are in series, while the capacitor is in parallel with this combination.
- Participants propose that the total impedance should be calculated symbolically before substituting numerical values, suggesting that the impedance of the inductor is represented as jωL.
- Some participants correct earlier claims about impedance addition, emphasizing that the series impedance of the resistor and inductor should be treated as R + jωL.
- There are attempts to derive expressions for the total current, with some participants suggesting that the total current can be calculated as the sum of the currents through the capacitor and the series R-L branch.
- Discussions include the need to handle complex numbers carefully, particularly when combining real and imaginary components in impedance calculations.
- Some participants express confusion about how to incorporate the capacitor's impedance into the overall calculations.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree on the need to calculate the total impedance and current in the circuit, but there are multiple competing views on the correct approach and the role of the capacitor in the calculations. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the best method to express the total current and how to handle the capacitor's contribution.
Contextual Notes
Limitations include the potential for algebraic errors and the challenge of managing complex numbers in impedance calculations. Some participants note that the circuit diagram is not visible to all, which may hinder understanding.