11thHeaven
- 48
- 0
Hi all, I'm working through a derivation of the general relationship between Cp and Cv and there's one point which is confusing me.
I understand that
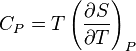
and
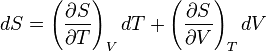
and that this implies the following:
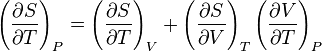
but isn't this equal to 0? Shouldn't the two partial derivatives on the right hand side, by the cyclic rule, multiply to -(∂S/∂T)V?
I know that I'm missing something here but I can't work out what it is.
Help appreciated!
I understand that
and
and that this implies the following:
but isn't this equal to 0? Shouldn't the two partial derivatives on the right hand side, by the cyclic rule, multiply to -(∂S/∂T)V?
I know that I'm missing something here but I can't work out what it is.
Help appreciated!