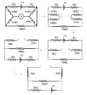
SUMMARY
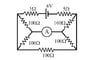
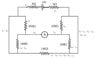
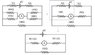
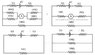
The discussion focuses on calculating the current through an ammeter in an electric circuit using Thevenin's theorem and current division principles. Participants clarify the relationship between resistors, specifically two 100Ω resistors in parallel, and the impact of a 50Ω resistor on the overall circuit. The final calculated current through the ammeter is confirmed to be 50.0 mA, derived from the equivalent Thevenin voltage (VTh = 5.45 V) and resistance (RTh = 100.909 Ω). The conversation emphasizes the importance of simplifying circuits for easier analysis.
PREREQUISITES
- Thevenin's theorem
- Current division in parallel circuits
- Equivalent resistance calculations
- Basic circuit analysis techniques
NEXT STEPS
- Study Thevenin's theorem applications in circuit analysis
- Learn about current division and its practical applications
- Practice calculating equivalent resistance in complex circuits
- Explore advanced circuit simplification techniques
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and anyone involved in analyzing or designing electrical circuits will benefit from this discussion.