- #1
stevenwright
- 1
- 0
This is my first post, and I hope I've found the right area to pose my question. As background, I don't have very much experience with HID applications, though I have extensive experience with general electrical wiring and systems design.
My question is this:
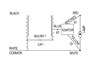
The difference between a metal halide transformer and a high pressure sodium transformer is that an HPS 'ballast' has an igniter to keep the arch tube lit, while a MH does not. Some manufacturers sell ballasts that can handle both types of bulbs, and have a switch which drops the igniter out of circuit for MH or includes it in circuit for HPS bulbs.
While there are slight differences between the electrical outputs of regular HPS and MH cores, they are not outside of the operational limits of either bulb. Thus the 'switchable' transformers.
What I don't understand is why a metal halide core can't be used to operate HPS lamps. Obviously, to run a MH lamp with an HPS ballast you take the igniter out of circuit. But where would you add an igniter in an MH ballast?
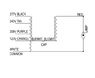
The schematics describe the igniter being attached between the "X3" wire and the lamp wire. I believe that simply attaching an igniter in line with the lamp wire on a MH will allow an HPS lamp to be operated. My theory being that the "X3" is simply an extension of the lamp wire.
Am I totally off base here? Can someone please help me with this question? Thank you very much, and I'm glad to have found such a wealth of information.
My question is this:
The difference between a metal halide transformer and a high pressure sodium transformer is that an HPS 'ballast' has an igniter to keep the arch tube lit, while a MH does not. Some manufacturers sell ballasts that can handle both types of bulbs, and have a switch which drops the igniter out of circuit for MH or includes it in circuit for HPS bulbs.
While there are slight differences between the electrical outputs of regular HPS and MH cores, they are not outside of the operational limits of either bulb. Thus the 'switchable' transformers.
What I don't understand is why a metal halide core can't be used to operate HPS lamps. Obviously, to run a MH lamp with an HPS ballast you take the igniter out of circuit. But where would you add an igniter in an MH ballast?
The schematics describe the igniter being attached between the "X3" wire and the lamp wire. I believe that simply attaching an igniter in line with the lamp wire on a MH will allow an HPS lamp to be operated. My theory being that the "X3" is simply an extension of the lamp wire.
Am I totally off base here? Can someone please help me with this question? Thank you very much, and I'm glad to have found such a wealth of information.