tw336
- 4
- 0
- Homework Statement
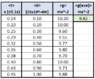
- In an experiment to determine the acceleration due to gravity close to the Earth’s surface g, the time t taken for a steel ball, released from an electromagnetic connector, to fall a vertical distance y was measured. The results are given in Table 1.
a) Use the results to calculate an experimental value of g and compare this to the expected value.
- Relevant Equations
- g=2*(x/t^2)
Hello there! This is my first post, so I apologise for any faux pas I am about to commit.
I have recently bumped into a few situations where I'm uncertain about my uncertainties. Especially where the value is a product of multiple variables.
Please see the attatched table, where g is a function of time and distance. I have used kinematic equations to solve for g (g=2*(x/T^2)). What would be the correct/appropriate method for calculating the uncertainty in the mean of g?
Can I look to find the standard deviation and error, and call the error the uncertainty in my mean? The data is not normally distributed.
Or do I need to propogate the uncertainties as a function of distance and time? g=f(T,d)
Any help would be greatly appreciated,
Thanks in advance,
T
I have recently bumped into a few situations where I'm uncertain about my uncertainties. Especially where the value is a product of multiple variables.
Please see the attatched table, where g is a function of time and distance. I have used kinematic equations to solve for g (g=2*(x/T^2)). What would be the correct/appropriate method for calculating the uncertainty in the mean of g?
Can I look to find the standard deviation and error, and call the error the uncertainty in my mean? The data is not normally distributed.
Or do I need to propogate the uncertainties as a function of distance and time? g=f(T,d)
Any help would be greatly appreciated,
Thanks in advance,
T
 !
!