Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the calculation of the C/N (Carrier-to-Noise ratio) in the context of digital communications, specifically relating to Bit Error Rate (BER), signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and modulation schemes such as QPSK. Participants are exploring how to approach a problem involving these concepts without complete information on bandwidth or data rate.
Discussion Character
- Homework-related
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
Main Points Raised
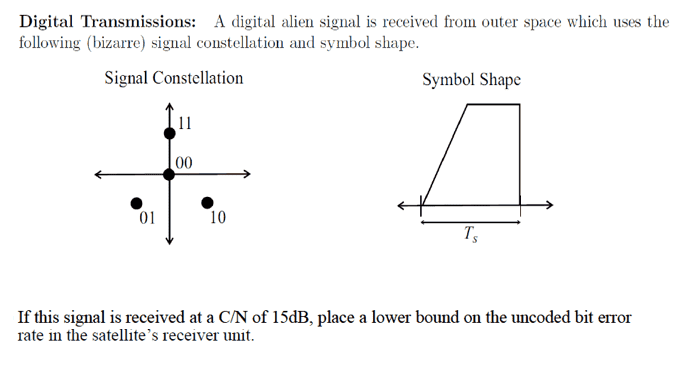
- One participant expresses uncertainty about how to approach the problem, noting the relationship between C/N and SNR (Eb/N0) but lacking necessary parameters such as bandwidth or data rate.
- Another participant reiterates the need for more information to solve the problem and suggests that the constellation diagram indicates a QPSK modulation scheme, although this is not confirmed.
- A participant mentions the potential to show the entire problem but believes it may be irrelevant, focusing instead on sketching voltage signals for an IQ-modulator and discussing drawbacks related to pulse shape.
- One participant proposes a method for calculating signal amplitude and noise, suggesting that the decision threshold for the detector is equal to the RMS noise amplitude, leading to a situation where the detector cannot decode data.
- There is an acknowledgment of uncertainty in calculations and a reference to various websites discussing C/N and BER for different modulation schemes.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants do not reach a consensus, as there are multiple uncertainties regarding the problem's parameters and the calculations involved. The discussion remains unresolved with differing viewpoints on how to proceed.
Contextual Notes
Limitations include missing assumptions about bandwidth and data rate, as well as unresolved mathematical steps in the calculations presented by participants.