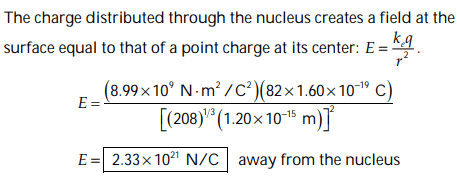SUMMARY
The electric field at the surface of the lead-208 nucleus is determined using the formula for the radius, given by r = (208)^{1/3}(1.20 × 10^{-15} m). This relationship arises from the volume comparison between the nucleus and the proton, expressed as V = 208 V_p. The derivation involves equating the volumes of the nucleus and proton, leading to the conclusion that r = (208R^3)^{1/3} and subsequently r = 208^{1/3}R.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of nuclear physics concepts, specifically nuclear volume.
- Familiarity with the formula for the volume of a sphere, V = (4/3)πr^3.
- Knowledge of the properties of lead-208 and its nuclear structure.
- Basic grasp of dimensional analysis in physics.
NEXT STEPS
- Research the properties of lead-208 and its nuclear characteristics.
- Study the derivation of nuclear volume relationships in different isotopes.
- Learn about the significance of nuclear radius in nuclear physics.
- Explore the concept of electric fields in nuclear physics and their calculations.
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in nuclear physics, physicists studying nuclear structure, and educators teaching advanced physics concepts related to nuclear properties.