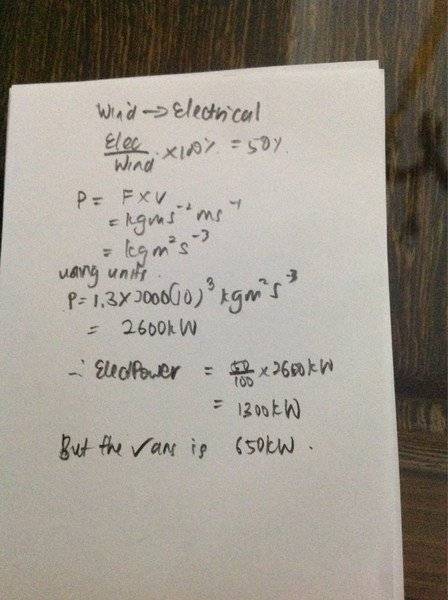SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on calculating power and efficiency in the context of A-level physics, specifically regarding wind energy. The relevant formula for efficiency is given as p(out) / p(in) x 100 percent. The correct approach involves using the formula for power, P = F x v, but the user struggles with missing values for force (F) and velocity (v). The correct method involves understanding that power can also be derived from wind energy using the formula 1/2 m v^2, where mass (m) is derived from the area and wind speed.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic physics concepts such as power, force, and velocity.
- Familiarity with the formula for efficiency in energy calculations.
- Knowledge of wind energy principles and how to calculate it.
- Ability to manipulate equations to derive missing variables.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of wind power equations, focusing on 1/2 m v^2.
- Learn how to calculate mass from wind density and area.
- Explore the concept of efficiency in energy systems and its calculations.
- Review the relationship between force, velocity, and power in physics.
USEFUL FOR
Students studying A-level physics, educators teaching energy concepts, and anyone interested in understanding wind energy calculations and efficiency metrics.