SUMMARY
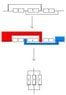
The discussion focuses on calculating the equivalent resistance of a purely resistive network consisting of three 6-ohm resistors connected in parallel between points X1 and X2. The correct equivalent resistance is determined to be 2 ohms when applying Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's Current Law. Participants emphasize the importance of visualizing the circuit diagram accurately, using color coding to clarify connections. The final consensus confirms that the effective resistance is indeed 2 ohms when the resistors are configured as described.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Ohm's Law
- Familiarity with Kirchhoff's Current Law
- Knowledge of series and parallel resistor configurations
- Ability to interpret circuit diagrams
NEXT STEPS
- Study the application of Ohm's Law in complex circuits
- Learn about Kirchhoff's Laws in electrical circuits
- Explore techniques for simplifying circuit diagrams
- Investigate the effects of varying resistor values in parallel configurations
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and anyone involved in analyzing or designing resistive networks will benefit from this discussion.