- #1
erandall
- 5
- 0
1. I'm a middle school science teacher without a science or math background. My goal here is to avoid teaching an explanation that kids will have to unlearn later in their academic career. I'm designing a lesson to teach students how to answer this question:
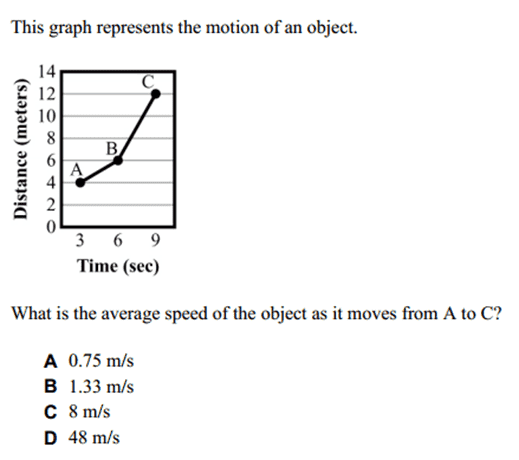 2. Limitation: students are NOT expected to understand velocity, they only need to manipulate the Speed= distance/time equation.
2. Limitation: students are NOT expected to understand velocity, they only need to manipulate the Speed= distance/time equation.
3. As far as I can tell from the answer choices, the answer should be 1.33 m/s, which is the ending speed. Logically, this makes sense to me: if the object was able to travel 12 meters in 9 seconds, then that final data point is essentially averaging the time that it takes to travel the total distance, despite any changes in rate that may occur throughout the line.
However, I seem to remember--and googling seems to confirm-- that this isn't actually the way mathematically to find the average slope of a function. So why does this work? Or am I actually incorrect about the answer?
If possible, could you please explain in terms that would make sense to a student who hasn't had a math or science education beyond the 6th grade. The more simple and concrete, the better!
Thanks for your help.
3. As far as I can tell from the answer choices, the answer should be 1.33 m/s, which is the ending speed. Logically, this makes sense to me: if the object was able to travel 12 meters in 9 seconds, then that final data point is essentially averaging the time that it takes to travel the total distance, despite any changes in rate that may occur throughout the line.
However, I seem to remember--and googling seems to confirm-- that this isn't actually the way mathematically to find the average slope of a function. So why does this work? Or am I actually incorrect about the answer?
If possible, could you please explain in terms that would make sense to a student who hasn't had a math or science education beyond the 6th grade. The more simple and concrete, the better!
Thanks for your help.