- #1
morgane28v
- 3
- 0
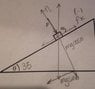
The coefficient of static friction between the crate m1=3.00kg and the incline with θ=35° shown in the figure below is .300. What minimum force F must be applied to the crate perpendicular to the incline to prevent the crate from sliding down the incline?
mgsinθ
μsmgcosθ
f=ma
I don't quite get how the applied force fits into the equation. mgsinθ-μsmgcosθ+F=0?