- #1
JohnnyLaws
- 10
- 0
- Homework Statement
- Basically, we have two stationary charged particles. The distance between them is 'd.' We know that they have the same charge of 2*10^-6. The objective is to calculate the distance at which the electric field is zero.
- Relevant Equations
- I think the equation we need is the electric field equation: E = k*q/(r^2), where k = 8.988 x 10^9 Nm^2/C^2, and 'r' is the distance between a point and the charge that is producing the field
This is the outline of the exercise I did on paper.
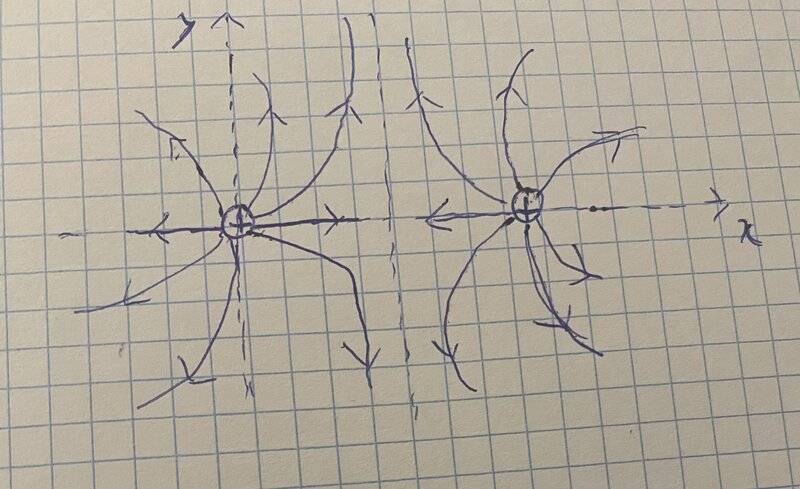
So basically, my attempt to solve this involved writing the equations according to the reference frame I chose. The origin is the first charge.
I began by putting the equations on paper:
E = 0=> k*q*1/(x^2)+k*q*1/((x+d))^2 = 0, Note that 'x + d' represents the distance between a point and the second charge.
After solving for 'x,' I obtained a strange result. Following that, I began to manipulate the initial condition, and instead of writing the electric field produced by the first charge with a positive sign, I used a minus sign, and I obtained the correct answer: 'x = d/2'
What I don't understand is why this is working, considering that all particles are positively charged. Shouldn't the electric field always be positive when charges have the same sign?
So basically, my attempt to solve this involved writing the equations according to the reference frame I chose. The origin is the first charge.
I began by putting the equations on paper:
E = 0=> k*q*1/(x^2)+k*q*1/((x+d))^2 = 0, Note that 'x + d' represents the distance between a point and the second charge.
After solving for 'x,' I obtained a strange result. Following that, I began to manipulate the initial condition, and instead of writing the electric field produced by the first charge with a positive sign, I used a minus sign, and I obtained the correct answer: 'x = d/2'
What I don't understand is why this is working, considering that all particles are positively charged. Shouldn't the electric field always be positive when charges have the same sign?