- #1
- 1,108
- 623
From this article on the monitoring of the solar Lyman Alpha emission line, a diagram (attached below) shows the 'mother of all absorption wavelength measurements': namely the geo coronal absorption of solar Lyman Alpha radiation at 1215.664 A or 121.5664 nm.
Is this still the most accurate measure of geo coronal absorption of solar Lyman Alpha ?
More recent related scientific articles are more concerned with trying to 'factor out' geo coronal absorption so they can see the 'true' profile of solar Lyman Alpha emission. So they don't pay much attention to the geo coronal absorption frequency itself. And yet I would say it is a very important frequency reference which should be measured as accurately as possible. It's value appears to be a tad lower than 121.56701 nm (NIST) which seems to result from a terrestrial emission (rather than absorption) measurement.
A more recent (1978) solar Lyman Alpha profile is this one from Artzner. But for some reason he does not specifically state a wavelength for the central geo-coronal absorption mininum. So the only data I am able to find on that is from the above 1969 article whence the graphic below originates.
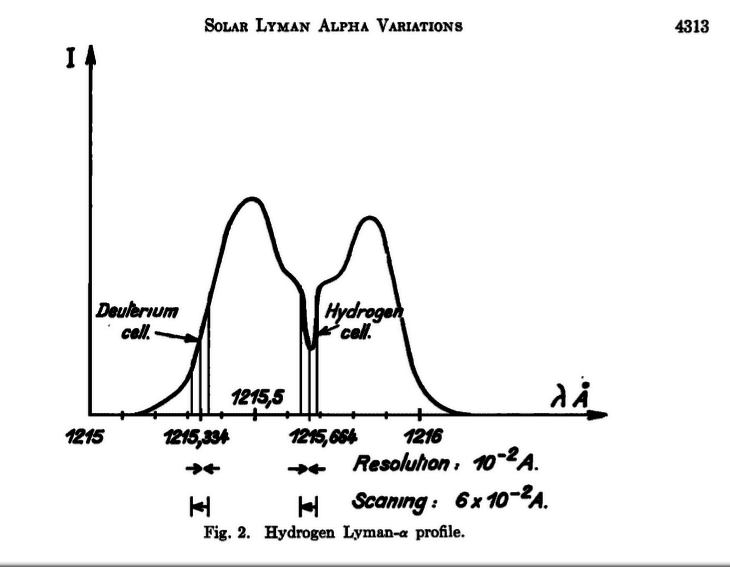
Is this still the most accurate measure of geo coronal absorption of solar Lyman Alpha ?
More recent related scientific articles are more concerned with trying to 'factor out' geo coronal absorption so they can see the 'true' profile of solar Lyman Alpha emission. So they don't pay much attention to the geo coronal absorption frequency itself. And yet I would say it is a very important frequency reference which should be measured as accurately as possible. It's value appears to be a tad lower than 121.56701 nm (NIST) which seems to result from a terrestrial emission (rather than absorption) measurement.
A more recent (1978) solar Lyman Alpha profile is this one from Artzner. But for some reason he does not specifically state a wavelength for the central geo-coronal absorption mininum. So the only data I am able to find on that is from the above 1969 article whence the graphic below originates.