- #1
KraakeCrest
- 18
- 2
Hi
Got some questions regarding grounding transformers (wye-delta), or maybe I should write, I need someone to tell me if my understanding is correct.
First, under no fault operation:
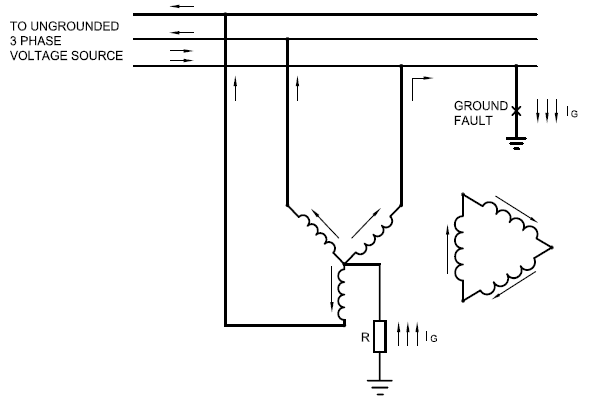
Only a small current will flow in the wye side of the grounding transformer, aka magnetizing current. Because, if the system is balanced, no other current will flow in the wye side, because amp-turns must be balanced (except magnetizing current), and since using KVL around the delta loop yields 0 there are no place for any currents in wye to be "amp-turn balanced". Conclusion: Only a small current is flowing in the wye primary side of the grounding transformer during balanced non-fault operation.During single phase to ground fault:
Because of the single phase to ground fault, zero sequence currents arise. For them to flow they require a return path via neutral or ground back to the source, which is provided by the wye-delta grounding transformer. So for zero sequence current to flow as shown in the picture below, the amp-turns on the wye side of the grounding transformer must be balanced by something. And this something is the delta secondary connection, using KVL around the loop with zero sequence induced voltages, yields something different from zero, and hence currents can flow in the closed loop and amp-turns are balanced.
Without this delta secondary and only a wye primary the grounding transformer would not add anything useful and only draw useless magnetizing current, right?
WYE-DELTA
Got some questions regarding grounding transformers (wye-delta), or maybe I should write, I need someone to tell me if my understanding is correct.
First, under no fault operation:
Only a small current will flow in the wye side of the grounding transformer, aka magnetizing current. Because, if the system is balanced, no other current will flow in the wye side, because amp-turns must be balanced (except magnetizing current), and since using KVL around the delta loop yields 0 there are no place for any currents in wye to be "amp-turn balanced". Conclusion: Only a small current is flowing in the wye primary side of the grounding transformer during balanced non-fault operation.During single phase to ground fault:
Because of the single phase to ground fault, zero sequence currents arise. For them to flow they require a return path via neutral or ground back to the source, which is provided by the wye-delta grounding transformer. So for zero sequence current to flow as shown in the picture below, the amp-turns on the wye side of the grounding transformer must be balanced by something. And this something is the delta secondary connection, using KVL around the loop with zero sequence induced voltages, yields something different from zero, and hence currents can flow in the closed loop and amp-turns are balanced.
Without this delta secondary and only a wye primary the grounding transformer would not add anything useful and only draw useless magnetizing current, right?
WYE-DELTA