SUMMARY
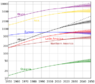
The discussion centers on the projected global population reaching 20 billion by 2050 and the implications for food production. Participants argue that this figure is exaggerated, with estimates suggesting a more realistic population of 7 to 10 billion. Key solutions proposed include the adoption of modern farming techniques, genetic modification of crops for climate resilience, and the development of in-vitro meat technologies. The conversation emphasizes the need for sustainable practices to address food production challenges amid climate change and diminishing arable land.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of modern farming techniques and their impact on food production
- Knowledge of genetic modification and its applications in agriculture
- Familiarity with in-vitro meat production and its environmental benefits
- Awareness of climate change effects on agriculture and food security
NEXT STEPS
- Research advancements in genetic modification for drought-resistant crops
- Explore the viability and market potential of in-vitro meat technologies
- Investigate modern farming techniques that increase arable land efficiency
- Study the impact of climate change on global food production and strategies for mitigation
USEFUL FOR
Agricultural scientists, environmentalists, policymakers, and anyone involved in food production and sustainability efforts will benefit from this discussion.

 I had the same thought.
I had the same thought. 


 .Some people seem to forget... cows are pretty good, self propelled grass harvesters...
.Some people seem to forget... cows are pretty good, self propelled grass harvesters...


