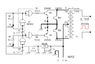
Power inverters convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) using key components such as transistors, capacitors, and oscillators. The primary transistors used are typically MOSFETs or IGBTs, which act as switches in the inverter's circuit. The conversion process involves a series of switches that create a waveform mimicking AC electricity through pulse width modulation. Inverters can vary in complexity, with designs ranging from simple square wave types to more advanced systems producing cleaner sine waves. Understanding these components and their functions is essential for effective use and application of power inverters.