Hardik Batra
- 130
- 5
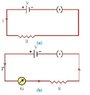
To make ammeter,
Resistance of proper small value is joined in parallel to the coil of galvanometer.This resistance is called a shunt.
For smaller resistance value,
We can not use the smallest resistance wire that is directly wound on coil of galvanometer so the resistance will become minimum.?
Resistance of proper small value is joined in parallel to the coil of galvanometer.This resistance is called a shunt.
For smaller resistance value,
We can not use the smallest resistance wire that is directly wound on coil of galvanometer so the resistance will become minimum.?