- #1
Volcano
- 147
- 0
Hi,
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transformer
related picture:
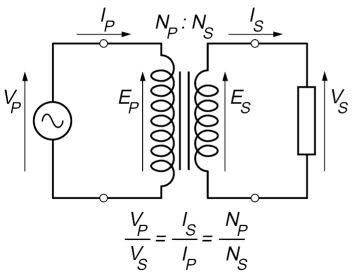
Above link, says: "If the voltage is increased, then the current is decreased by the same factor."
I didn't understand. Is this means, if I increase Vp, Ip will decrease? Or means Is will decrease?
One more... Suppose an ideal transformer. Vp/Vs , Np/Ns and Is/Ip ratios are equal(like given pic). If I increase Vp then Vs will too because Np/Ns ratio is constant. So, Vp/Vs ratio will be equal to Np/Np everytime. Let's suppose, load resistance is variable(potentiometer) and resistance is increasing;
1. Vs won't change. Because Vp, Np, Ns didn't change.
2. Is will decrease. Because Vs = Is * R(Ohm Law).
3. Ip will decrease like Is.
As a result: If transformer is ideal and ONLY load(resistance) decrease, neither Vp nor Vs don't change. Only both Ip and Is decrease. Surely if load(resistance) increase both circuits decrease but both voltages stay the same.
Am I right?
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transformer
related picture:
Above link, says: "If the voltage is increased, then the current is decreased by the same factor."
I didn't understand. Is this means, if I increase Vp, Ip will decrease? Or means Is will decrease?
One more... Suppose an ideal transformer. Vp/Vs , Np/Ns and Is/Ip ratios are equal(like given pic). If I increase Vp then Vs will too because Np/Ns ratio is constant. So, Vp/Vs ratio will be equal to Np/Np everytime. Let's suppose, load resistance is variable(potentiometer) and resistance is increasing;
1. Vs won't change. Because Vp, Np, Ns didn't change.
2. Is will decrease. Because Vs = Is * R(Ohm Law).
3. Ip will decrease like Is.
As a result: If transformer is ideal and ONLY load(resistance) decrease, neither Vp nor Vs don't change. Only both Ip and Is decrease. Surely if load(resistance) increase both circuits decrease but both voltages stay the same.
Am I right?
Last edited: