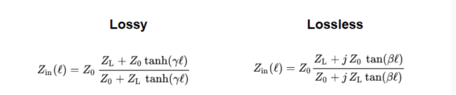Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the calculation of input impedance for transmission lines, particularly when considering segments of varying lengths and configurations. Participants explore whether to integrate or divide the input impedance when dealing with transmission lines in series, addressing both theoretical and practical implications.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- Some participants suggest calculating the total impedance of a transmission line segment and dividing it by the characteristic impedance to derive the number of segments.
- Others propose that the input impedance is dependent on both length and frequency, indicating that changing the location of divided parts may yield different results across the frequency spectrum.
- A participant mentions that the input impedance equation would change for a lossy line compared to a lossless line.
- There is a suggestion to use iterative methods to calculate the overall input impedance by considering each section of the transmission line and its load impedance.
- Some participants express the need for equations that show the interrelations of separate parts of the transmission line, particularly in practical scenarios where multiple lines are connected.
- Concerns are raised about the challenges of reflections at interfaces with mismatched impedances when connecting different transmission line sections.
- One participant emphasizes the importance of maintaining impedance close to standard values (e.g., 50 Ohm) to minimize the effects of mismatches.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants do not reach a consensus on whether to integrate or divide the input impedance, and multiple competing views remain regarding the best approach to model the input impedance of transmission lines in series.
Contextual Notes
Participants note that the input impedance is influenced by various factors, including the characteristics of the transmission line (e.g., lossy vs. lossless) and the specific configurations of the segments. There are unresolved mathematical steps and dependencies on definitions that complicate the discussion.