- #1
Quds Akbar
- 124
- 6
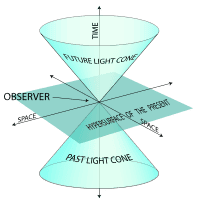
Is space-time flat and if the answer is yes then how can objects orbit vertically and diagonally(since gravity is the warping of space-time)? Or does it exist from all sides?
CaptCoonoor said:Space-time isn't flat,
If spacetime is absolutely flat, then if you were to set off in a rocket ship and travel in a single direction, you would eventually get to the universe that's just like the one you're in now, but where you got up an hour later this morning, or where Michael Jackson is still alive. And if you continued on this journey, eventually you would start getting to the other universes with basic physical laws, the other universes of the multiverse. What I believe is It's close to Flat, But not absolute flat
3D of Space Combine with 1D of Time to Form Malinowski space
Einstein in his book talked about this, Should read it..
CaptCoonoor said:3D of Space Combine with 1D of Time to Form Minkowski space
I meant he talked abut Minkowsi space and lorentz transformationMatterwave said:What? I don't think Einstein talked about multiple universes to which you could travel if space-time is flat...
http://www.amazon.com/dp/9380914229/?tag=pfamazon01-20Quds Akbar said:What is the book called?
Cool graphic, but isn't it curved the wrong way? Does the purple object have negative mass?Lamdbaenergy said: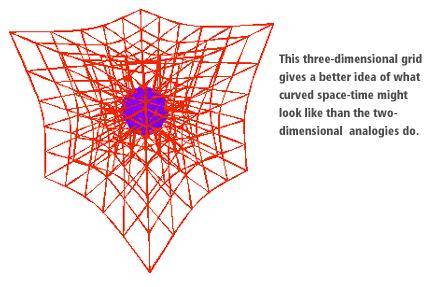
Spacetime is a concept in physics that combines the three dimensions of space and the dimension of time into a single four-dimensional continuum. Whether it is truly flat or not is a matter of debate among scientists. Some theories, such as general relativity, suggest that spacetime is curved by the presence of mass and energy, while other theories propose that it is indeed flat.
The curvature of spacetime plays a crucial role in the motion of orbiting objects. According to general relativity, the presence of massive objects, such as planets or stars, curves the spacetime around them. This curvature causes smaller objects, like satellites, to follow curved paths around the larger objects, rather than traveling in straight lines.
While we cannot directly observe the curvature of spacetime, we can indirectly measure its effects on objects, such as the orbit of planets and stars. Scientists also use gravitational lensing, where the light from distant objects is bent by the curvature of spacetime, to study the effects of spacetime curvature.
In general relativity, spacetime is described as being locally flat, meaning that in small regions of space it appears to be flat. However, on a larger scale, the presence of massive objects can cause spacetime to become curved in certain directions. This means that spacetime is not completely flat in all directions.
In general relativity, the concept of spacetime curvature explains the phenomenon of gravity. Instead of being a force between objects, gravity is described as the curvature of spacetime caused by the presence of mass and energy. This curvature determines the paths of objects, including the motion of planets and the orbit of the moon around the Earth.