You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Spacetime: Definition and 1000 Discussions
In physics, spacetime is any mathematical model which fuses the three dimensions of space and the one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why different observers perceive differently where and when events occur.
Until the 20th century, it was assumed that the three-dimensional geometry of the universe (its spatial expression in terms of coordinates, distances, and directions) was independent of one-dimensional time. The famous physicist Albert Einstein helped develop the idea of space-time as part of his theory of relativity. Prior to his pioneering work, scientists had two separate theories to explain physical phenomena: Isaac Newton's laws of physics described the motion of massive objects, while James Clerk Maxwell's electromagnetic models explained the properties of light. However, in 1905, Albert Einstein based a work on special relativity on two postulates:
The laws of physics are invariant (i.e., identical) in all inertial systems (i.e., non-accelerating frames of reference)
The speed of light in a vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of the light source.The logical consequence of taking these postulates together is the inseparable joining together of the four dimensions—hitherto assumed as independent—of space and time. Many counterintuitive consequences emerge: in addition to being independent of the motion of the light source, the speed of light is constant regardless of the frame of reference in which it is measured; the distances and even temporal ordering of pairs of events change when measured in different inertial frames of reference (this is the relativity of simultaneity); and the linear additivity of velocities no longer holds true.
Einstein framed his theory in terms of kinematics (the study of moving bodies). His theory was an advance over Lorentz's 1904 theory of electromagnetic phenomena and Poincaré's electrodynamic theory. Although these theories included equations identical to those that Einstein introduced (i.e., the Lorentz transformation), they were essentially ad hoc models proposed to explain the results of various experiments—including the famous Michelson–Morley interferometer experiment—that were extremely difficult to fit into existing paradigms.
In 1908, Hermann Minkowski—once one of the math professors of a young Einstein in Zürich—presented a geometric interpretation of special relativity that fused time and the three spatial dimensions of space into a single four-dimensional continuum now known as Minkowski space. A key feature of this interpretation is the formal definition of the spacetime interval. Although measurements of distance and time between events differ for measurements made in different reference frames, the spacetime interval is independent of the inertial frame of reference in which they are recorded.Minkowski's geometric interpretation of relativity was to prove vital to Einstein's development of his 1915 general theory of relativity, wherein he showed how mass and energy curve flat spacetime into a pseudo-Riemannian manifold.
View More On Wikipedia.org
Until the 20th century, it was assumed that the three-dimensional geometry of the universe (its spatial expression in terms of coordinates, distances, and directions) was independent of one-dimensional time. The famous physicist Albert Einstein helped develop the idea of space-time as part of his theory of relativity. Prior to his pioneering work, scientists had two separate theories to explain physical phenomena: Isaac Newton's laws of physics described the motion of massive objects, while James Clerk Maxwell's electromagnetic models explained the properties of light. However, in 1905, Albert Einstein based a work on special relativity on two postulates:
The laws of physics are invariant (i.e., identical) in all inertial systems (i.e., non-accelerating frames of reference)
The speed of light in a vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of the light source.The logical consequence of taking these postulates together is the inseparable joining together of the four dimensions—hitherto assumed as independent—of space and time. Many counterintuitive consequences emerge: in addition to being independent of the motion of the light source, the speed of light is constant regardless of the frame of reference in which it is measured; the distances and even temporal ordering of pairs of events change when measured in different inertial frames of reference (this is the relativity of simultaneity); and the linear additivity of velocities no longer holds true.
Einstein framed his theory in terms of kinematics (the study of moving bodies). His theory was an advance over Lorentz's 1904 theory of electromagnetic phenomena and Poincaré's electrodynamic theory. Although these theories included equations identical to those that Einstein introduced (i.e., the Lorentz transformation), they were essentially ad hoc models proposed to explain the results of various experiments—including the famous Michelson–Morley interferometer experiment—that were extremely difficult to fit into existing paradigms.
In 1908, Hermann Minkowski—once one of the math professors of a young Einstein in Zürich—presented a geometric interpretation of special relativity that fused time and the three spatial dimensions of space into a single four-dimensional continuum now known as Minkowski space. A key feature of this interpretation is the formal definition of the spacetime interval. Although measurements of distance and time between events differ for measurements made in different reference frames, the spacetime interval is independent of the inertial frame of reference in which they are recorded.Minkowski's geometric interpretation of relativity was to prove vital to Einstein's development of his 1915 general theory of relativity, wherein he showed how mass and energy curve flat spacetime into a pseudo-Riemannian manifold.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
S
I Is Vacuum Decay from a False to True State Impossible or Just Unlikely?
I found this paper (https://arxiv.org/pdf/hep-th/0211160.pdf) which argues against the possibility of a decay from a metastable vacuum to a true vacuum state. However, this is the first time I've read this. Is it then impossible that a vacuum decay from a false vacuum may occur (even in... -
S
I Holographic principle in continuous spacetime?
Can the holographic principle be applied to spacetimes and metrics that are (fundamentally) continuous/smooth? Or only to discrete ones?- Suekdccia
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Beyond the Standard Models
-

I Time dilation vs Differential aging vs Redshift
Hi, I would like to ask for a clarification about the terms time dilation vs differential aging vs gravitational redshit. As far as I can tell, time dilation is nothing but the rate of change of an object's proper time ##\tau## w.r.t. the coordinate time ##t## of a given coordinate chart (aka...- cianfa72
- Thread
- Replies: 21
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
P
I Curved spacetime bulging in time direction
Let us start with a simple two-dimensional space that is asymptotically flat, like e.g. sheet of paper on a desk. Geodesics in this space are straight lines in the traditional sense. Now add a bulge in the center of this space. without affecting the asymptotic flatness. Say, we simply distort...- pahenning
- Thread
- Replies: 30
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
L
I Are the Lorentz Transformations False?
Consider the Lorentz transformations with c=1, and consider any point in space whose x coordinate isn't zero, starting from ##t_{inital }= t'_{inital }=0## ##t' =\gamma (t-xv)## ##t= \frac { t'}{\gamma} + xv## ##\Delta t' = t'-0## ##\Delta t = t-0## Time dilation provides ##\Delta t' =\gamma...- Leepappas
- Thread
- Replies: 54
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B How do you project a Killing Vector onto a Schwarzschild field?
What is the math for projecting a Killing vector onto a Schwarzschild field of spacetime? How would you do it?- bobrubino
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Killing vector Spacetime
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Minkowski Spacetime vs Euclidean Spacetime
Which one would you use in order to map out a black hole and its connection to a white hole?- bobrubino
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Very basic questions about visualizing spacetime
I'd like to start with: Does the rubber sheet analogy still hold true enough? Or is there really no visualization (it's all mathematical constructs)? Does this picture analogy hold at all here? With the curved geodesics influencing the paths of things. Thanks!- jaketodd
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Spacetime Visualization
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B What does the Minkowski spacetime interval represent and how is it determined?
In the Minkowski space time equation in one dimensional space , ds^2 = dx^2 - (ct)^2, what is the value to use for x and t, and what does the space time interval ds represent? For example, if Alpha Centauri is 4 light years away, what values are. used for x and t, based on speed I guess, and...- PhanthomJay
- Thread
- Replies: 20
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Newton Galilean spacetime as fiber bundle
Hi, Penrose in his book "The Road to Reality" claims that Newton/Galilean spacetime has actually a structure of fiber bundle. The base is one-dimensional Euclidean space (time) and each fiber is a copy of ##\mathbb E^3##. The projection on the base space is the "universal time mapping" that...- cianfa72
- Thread
- Replies: 29
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
B
B Gravitational Field of a System: Exploring the Curves of Spacetime
Hey, if I take two objects for Example the Earth and Moon and treat them as a gravitational bound “system”. The Earth and Moon have their own local curves in spacetime. Can I use/treat the whole “system” as a curve in spacetime? For example, a curve that includes all objects of the “system”...- BeedS
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
B How do space and time fuse together to form “spacetime?”
Here is the definition of spacetime? “In physics, spacetime is any mathematical model that fuses the three dimensions of space and the one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional continuum.” But if space is literally the absence of matter or physical properties, and time has no...- Wiredcerebellum
- Thread
- Replies: 37
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
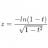
I Asymmetry in Length contraction?
Instead of a twin paradox, let’s just consider an inbound starship approaching Earth at relativistic speed. The traveler is on a flyby mission, he will never change speed or direction. We will disagree with the traveler on how much time will have elapsed when he passes Earth. The discrepancy can...- substitute materials
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Force carrier particle trajectories and warped spacetime
Do force carriers follow the curvature of spacetime, or do they travel in perfectly straight lines? With black holes, gravity of course exists, so I'm thinking the force carriers (at least gravitons) don't follow spacetime curvature, since they would never escape the event horizon. Sounds like...- jaketodd
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
S
B How does gravity's warping of spacetime appear first among the forces?
The Wikipedia section below says that gravity is the earliest to appear out of the fundamental interactions, but wasn't high energy in every area already curving its local spacetime surroundings? https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chronology_of_the_universe#The_very_early_universe -
P
B How to Add Metres & Seconds for Equal ds2: Einstein's Theory
Reading this PDF from Professor Richard Conn Henry, I am confused by the multiplication by c on page 2. x, y and z are metres. t has units seconds. So I would think, "We can't subtract seconds from metres , we can't subtract dt from dx." To sidestep that, Einstein multiplied dt by c. c has...- Pedroski55
- Thread
- Replies: 22
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B What is the metric for a bag-of-gold spacetime?
What is the metric for a bag-of-gold spacetime?- Onyx
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
D
What is the Role of Physics in Understanding the World Around Us?
Hi, Thanks for having me as a member. I've had a lifelong interest in science, all types of science but particularly in physics. It's the basis of everything isn't it? Biology is based on chemistry, chemistry is based on physics, physics is based on quantum physics and that is based...- Doug Horrigan
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: New Member Introductions
-

B Faster Than Light Travel: Exploring the Possibilities of Spacetime Curvature
Based on the current understanding of general relativity, it is possible that curving spacetime in the back of a spacecraft would allow for faster-than-light travel. In general relativity, the curvature of spacetime is determined by the universe's distribution of matter and energy. If a...- Marcarious Thomas
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Research on conservation of spacetime curvature
After trying to kinda get a picture of the field of play in quantum physics according to the standard model, a question came up. I tried to formulate the known bosons each as a particle transferring some property. 1. Photons transfer electric charge: the electromagnetic force gives attraction...- Structure seeker
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Cosmology
-

I Worldlines & Curves in Spacetime: Exploring Possibilities
Can there be worldlines that are neither timelike, nor null, nor spacelike? They can Are there curves in spacetime that are neither timelike, nor null, nor spacelike? Why?- SaintRodriguez
- Thread
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Calculating Spacetime Intervals for Simultaneous Events
Exercise: My solutions: For events to be simultaneous, the invariant interval must be bigger than zero (spacelike). I got $$I = -c^2 \Delta t^2 + \Delta x^2 + \Delta y^2 + \Delta z^2 = -(0-1)^2 + (0-2)^2 + (0-0)^2 + (0-0)^2 = -1 + 4 = 3 >0$$. Which is indeed greater than zero, to find the...- milkism
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
I Are there non-smooth metrics for spacetime (without singularities)?
Are there non-smooth metrics for spacetime (that don't involve singularities)? I found this statement in a discussion about the application of local Lorentz symmetry in spacetime metrics: Lorentz invariance holds locally in GR, but you're right that it no longer applies globally when gravity... -
S
I Approximate local flatness = Approximate local symmetries?
Pseudo-Riemannian manifolds (such as spacetime) are locally Minkowskian and this is very important for relativity since even in a highly curved spacetime, one could locally approximate the spacetime into a flat minkowski one. However, this would be an approximation. Perhaps this is a naive... -
S
I Solutions that break the Lorentz invariance...?
I was reading a discussion where some physicists participated* where the topic of Lorentz invariance violations occurring in cosmology is mentioned. There, they mention that we can imagine a Lorentz-violating solution to the cosmological equations. What do they mean by that? Can anyone specify... -
S
I Inhomogeneities and topological defects in cosmology...
I have heard that some types of inhomogeneties and topological defects (like cosmic strings) in cosmology have been proposed to be able to break fundamental symmetries of nature such as the Poincaré, Lorentz, diffeomorphism CPT, spatial/time translational...etc symmetries... However, I have not... -
S
I What does it mean that symmetries do not hold globally?
Perhaps this is a stupid question but, if Lorentz symmetry and time translational symmetry are not global in an expanding universe, wouldn't that mean that is possible that other Hubble spheres outside our observable universe could have other symmetries or an absence of the Lorentz symmetry? I... -
S
I Explore Spacetimes, Metrics & Symmetries in Relativity Theory
I was discussing this paper with a couple of physicists colleagues of mine (https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.12970) In the paper, the authors describe "spacetimes without symmetries". When I mentioned that, one of my friends said that no spacetime predicted or included in the theory of relativity...- Suekdccia
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
I No Symmetry Spacetimes/Metrics in Theory of Relativity
In the context of the Theory of Relativity are there any spacetimes or metrics with a complete absence of symmetries? I mean, consider a type of space or metric where no symmetries would hold (at least not exactly, but approximately). A space or metric where the Poincaré invariance (including...- Suekdccia
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
L
A Going from Cauchy Stress Tensor to GR's Energy Momentum Tensor
Why do the Cauchy Stress Tensor & the Energy Momentum Tensor have the same SI units? Shouldn't adding time as a dimension changes the Energy Momentum Tensor's units? Did Einstein start with the Cauchy Tensor when he started working on the right hand side of the field equations of GR? If so, What... -

B Shouldn't quantum gravity be an interaction between mass and spacetime?
Einstein showed (via general relativity) that spacetime is curved by mass, mass moves in relation to this curvature, and that gravitation arises as secondary effect. Why then are we looking for quantum gravity as some sort of mass<->mass interaction? Aren't the fundamental interactions better...- TerranIV
- Thread
- Replies: 40
- Forum: Beyond the Standard Models
-
S
I Can gravitational waves gain energy in an expanding FRW spacetime?
I was reading this paper (*Green's functions for gravitational waves in FRW spacetimes:* [https://arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9309025](https://arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9309025)) and I had a specific question about one statement in the paper that I would like to ask: At page 6, the author says that... -
S
I How fast does the particle go through spacetime?
This is a very basic question, and I am not sure I have the answer. A photon goes from point A to point B, only 1 meter distance apart from each other. A spacetime diagram would show a line connecting points A and B at a 45 degree angle. This can be a right triangle with equal sides, with...- student34
- Thread
- Replies: 20
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
G
I Magnetic Field vs Spacetime: Effects on Inertia Disk
By following article a magnetic field can produce a least a minimum distortion in spacetime. If we have a inertia disk spinning 50% inside of a strong closed magnetic field may we suppose that we will create an unbalanced in the angular disc moment producing a propulsion without mass variation...- Gitirana
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

A Propagation Vector of Light in Kerr Spacetime: Reference Needed
Hi, there. I am currently reading the paper, Gravitational Faraday rotation induced by a Kerr black hole (https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.38.472). After Eq. (2.4), it reads that The paper does not provide the derivation of the equations and no related reference is listed. Also, ##k^i## is not...- Haorong Wu
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Distance b/w 2 Points on Spacetime Diagrams: Meaning?
With one spatial dimension ## x ##, the spacetime interval between two events ## A ## and ## B ## is ## \Delta s= \sqrt{(ct_{B}-ct_{A})^{2}-(x_{B}-x_{A})^{2}} ## I have a technical question: on the plane of the graph (x,y=ct), the ordinary distance between 2 points ## A ## and ## B ## is ##...- Kairos
- Thread
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
N
I Do AEST (Absolute Euclidean Spacetime) models work?
I was reading a paper by J.M.C Montanus which was published in <low quality journal reference removed> in which he claims under AEST the new gravitational dynamics and electrodynamics are reformulated in close correspondence with classical physics, and subsequently leads to the correct...- name123
- Thread
- Replies: 83
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

What should I do with my spacetime model?
I created a model of spacetime based on an extension I added to the principle of relativity. I then derived the coordinate transformations which preserve the speed of light in all frames, which are different from the Lorentz transformation. I worked out the formulae for energy and momentum, and...- Ahmed1029
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: General Discussion
-

I Calculating Spacetime Around Multiple Objects
In describing the spacetime around a massive, spherical object, one would use the Schwarzschild Metric. What metric would instead be used to describe the spacetime around multiple massive bodies? Say, for example, you want to calculate the Gravitational Time Dilation experienced by a rocket ship...- Sciencemaster
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
I Can there be some kind of photon emission caused by space expansion?
Are there any kind of observed and experimentally verified processes or mechanisms where photon emission occurs and which are directly cause by spacetime expansion in some way? -
E
A What is the formal definition of spacetime in physics?
What is the mathematical definition of spacetime here?- Enrico
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Spacetime
- Replies: 61
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
I Matter Gaining Energy from Expanding Spacetime?
Sean Carroll has an article (https://www.preposterousuniverse.com/blog/2010/02/22/energy-is-not-conserved/) where he explains that matter can gain energy from spacetime expansion. At the end of the article, he says: In general relativity spacetime can give energy to matter, or absorb it from...- Suekdccia
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
P
B Exploring Mass, Gravity & SpaceTime: Ask for Expertise Here
Greetings. I registered to this forum because of a particular issue regarding Gravity. I'm no astrophysicist or mathematician, i searched to find an answer, but the terminology and equations are a little much for me. I feel the best direct way is to ask people with the right expertise. It is...- Palasta
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Gravity Mass Relaitivity Spacetime
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
H
I Spacetime interval and basic properties of light
While not having a professional physics background I was still interested in knowing more about special and general relativity. Therefore I was trying to find out where the space time interval was coming from in relation to the speed of light. Of course this is the first point to start I...- HansH
- Thread
- Replies: 141
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Could the source of dark energy be our parent black hole feeding?
About a year ago, I heard Leonard Susskind discussing how entangled black holes could create spacetime. As I was listening to Prof. Susskind describe the mechanisms for creating entangled black holes, and how these black holes might create their own spacetime, it occurred to me that if we were...- Bob Walance
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Cosmology
-
C
I Calculating Relative Change in Travel Time Due to Spacetime Perturbation
Suppose you have the following situation: We have a spacetime that is asymptotically flat. At some position A which is in the region that is approximately flat, an observer sends out a photon (for simplicity, as I presume that any calculations involved here become easier if we consider a...- cicero
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
I Please help with my spacetime diagrams (relativity problem)
Here is a simple scenario where Object A and Object B cross past each other on an x-axis (for simplicity sake, let's just assume that they somehow passed each other on one spatial dimension). As they cross past each other, a photon gets released in the positive direction, and then gets absorbed...- student34
- Thread
- Replies: 27
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
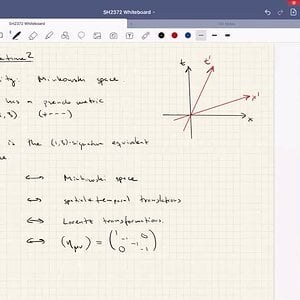
SH2372 General Relativity - Lecture 5
0:00 What is spacetime? 20:20 Kinematics, basic definitions 35:18 Motion of test particles 41:18 Frequency shift of light 1:10:19 Simultaneity- Orodruin
- Media item
- Doppler shift Redshift Simultaneity Spacetime
- Comments: 0
- Category: Relativity
-

I The curvature of space and curvature of spacetime
Hi, The quote below has been taken from this article, https://math.ucr.edu/home/baez/einstein/node2.html, which I came across. The quote doesn't make any sense to me, especially the part in boldface. Could you please help me with it?- PainterGuy
- Thread
- Replies: 21
- Forum: Cosmology
-
D
B Free Fall in Curved Spacetime: Does Minkowski Spacetime Exist?
This topic has been discussed in the past on this forum, however there is one point that seems to be unclear. One example of the setup is the following: The universe is at a stage where all the matter is concentrated in a single black hole, except two spacecraft s A and B that orbit it far...- DanAil
- Thread
- Replies: 21
- Forum: Special and General Relativity