Like Tony Stark
- 182
- 6
- Homework Statement
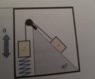
- Two bodies of equal mass are connected by an ideal rope and are inside a room which can accelerate vertically. The second body is attached to a spring of constant ##200 \frac{N}{m}##. Find the deformation of the spring when
A) the room moves with constant velocity
B) the room is accelerating upwards with ##2 \frac{m}{s^2}##.
C) the room is accelerating downwards with ##2 \frac{m}{s^2}##.
- Relevant Equations
- Newton's equations
I've solved all the cases in the non inertial system.
A) For ##m_1## we have
##x) P_{1x} -T=m.a_x##
##y) N_1 -P_{1y}=m.a_y##
For ##m_2## we have
##y) T+F_e -P_2=m.a_y##
As it moves with constant velocity I solve it setting ##a_x=0##. So for ##m_1## ##mgsin(\alpha)=T##, then I replace it in the tension of ##m_2## and find ##\Delta x##
B) For ##m_1##
##x) mgsin(\alpha)-f*.sin(\alpha)-T=0##
For ##m_2##
##y) Fe + T -mg-f*=0##
Where ##f*=2m##
Then, I replaced the tension from ##m_1## in ##m_2## and found the deformation. (As you see, I considered the elastic force pointing upwards in this case)
C) the same for ##B## just changing the sign of ##f*## and the elastic force.Is this right? Because I had some doubts about the sign of the elastic force.
A) For ##m_1## we have
##x) P_{1x} -T=m.a_x##
##y) N_1 -P_{1y}=m.a_y##
For ##m_2## we have
##y) T+F_e -P_2=m.a_y##
As it moves with constant velocity I solve it setting ##a_x=0##. So for ##m_1## ##mgsin(\alpha)=T##, then I replace it in the tension of ##m_2## and find ##\Delta x##
B) For ##m_1##
##x) mgsin(\alpha)-f*.sin(\alpha)-T=0##
For ##m_2##
##y) Fe + T -mg-f*=0##
Where ##f*=2m##
Then, I replaced the tension from ##m_1## in ##m_2## and found the deformation. (As you see, I considered the elastic force pointing upwards in this case)
C) the same for ##B## just changing the sign of ##f*## and the elastic force.Is this right? Because I had some doubts about the sign of the elastic force.
Attachments
Last edited: