- #1
JJ91
- 41
- 0
I'm not very familiar with all electronics (power engineering student) but this circuit especially qoes on my head for couple of days now:
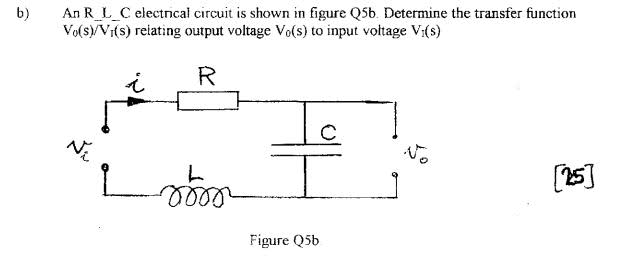
Haven't seen such topology but would this circuit change the phase of the supply current with respect to the output point ?
My task is to find a transfer function for this circuit thus I would like to get to know what is the exactly the name of this circuit and its task in electronic world ;)
Thanks,
Tom
Haven't seen such topology but would this circuit change the phase of the supply current with respect to the output point ?
My task is to find a transfer function for this circuit thus I would like to get to know what is the exactly the name of this circuit and its task in electronic world ;)
Thanks,
Tom