waterchan
- 23
- 0
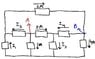
First of all, sorry for the poorly drawn figure.
In this figure, given are several conducting elements connecting by conducting wires, with the direction and amount of current flow indicated. I have to find the current across elements I1 through I4. When I apply Kirchoff's Current Law at node A (pointed to by the red arrow), I get:
Current entering node = Current leaving node
0 = I2 + 7A + 3A
I2 = -10A
Similarly, when I apply the law at node B (blue arrow), I get:
Current entering node = Current leaving node
2A = I4 + 4A
I4 = -2A
Am I doing something wrong, or is it possible for current to have a negative value depending on direction? In other words, can current be a vector quantity?
Thanks for regarding my dumb question.
In this figure, given are several conducting elements connecting by conducting wires, with the direction and amount of current flow indicated. I have to find the current across elements I1 through I4. When I apply Kirchoff's Current Law at node A (pointed to by the red arrow), I get:
Current entering node = Current leaving node
0 = I2 + 7A + 3A
I2 = -10A
Similarly, when I apply the law at node B (blue arrow), I get:
Current entering node = Current leaving node
2A = I4 + 4A
I4 = -2A
Am I doing something wrong, or is it possible for current to have a negative value depending on direction? In other words, can current be a vector quantity?
Thanks for regarding my dumb question.