Homework Help Overview
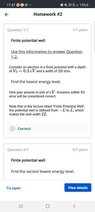
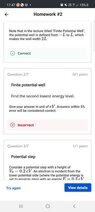
The discussion revolves around a physics homework problem involving an electron in a finite potential well characterized by a depth of V0=0.3 eV and a width of 10 nm. The original poster seeks assistance in finding the lowest and second lowest energy levels, expressing confusion over discrepancies with autograder feedback.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Assumption checking, Problem interpretation
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants discuss the application of the formula for energy levels, questioning whether the original poster is using the correct approach for a finite potential well versus an infinite one. There are inquiries about numerical techniques and the validity of the formulas being applied.
Discussion Status
Several participants have provided guidance on reviewing lecture materials and suggested looking into numerical methods for solving the problem. The original poster has been encouraged to share their calculations for further clarification, and there is ongoing exploration of different interpretations of the problem.
Contextual Notes
There is mention of specific constraints regarding the autograder's acceptance of answers within a 5% error margin, as well as the importance of showing work in LaTeX for clarity. Additionally, the discussion touches on the challenges of electronic homework systems in revealing students' problem-solving processes.