You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Me In What My Teacher Said Is Easy
- Thread starter Chikawakajones
- Start date
-
- Tags
- Teacher
AI Thread Summary
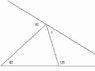
To find the value of x in the triangle problem, it is essential to apply the theorem that states the measure of an external angle equals the sum of the two opposite angles. Given that one of the opposite angles is 50 degrees, the angle adjacent to the external angle of 125 degrees can be calculated as 180 - 125. The next step involves using the supplementary angle property, where the sum of two angles on a straight line equals 180 degrees. Ultimately, the calculations lead to determining the value of x through geometric reasoning rather than specific formulas. Understanding these principles is crucial for solving the problem effectively.
Physics news on Phys.org
HallsofIvy
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 42,895
- 984
The sum of the three angles in a triangle is 180 degrees. The sum of two angles making a line is also 180 degrees: that leads to the well known theorem (it's probably in your text) that the measure of an external angle (here the one marked "125") is equal to the sum of the measures of the two opposite angles. One of those two opposite angles is 50 degrees. From that you can find the measure of the angle between "80" and "x" and then find x.
Chikawakajones
- 22
- 0
Are there any "formulas" to find "x" in this particular problem?...
Stargate
- 28
- 0
Not that I know of
dextercioby
Science Advisor
- 13,397
- 4,070
Chikawakajones said:Are there any "formulas" to find "x" in this particular problem?...
Beside this one
A+B+C=180°
,where A,B,C are the three angles of a plane triangle,nope.
But,as Ivy said,u need to know that the sum of two supplementary angles is 180°.
This is all u need to know to get it done.
Daniel.
derekmohammed
- 105
- 0
Again there are no formulas to solve this problem, it is all geometrical.
Step one.
Look at the angle 125. 180-125 will give you the angle on the other side of the line.
Step two add 55+50 and minus the product from 180. this is the upper angle.
Step three add 80+75 then minus that from 180 and that is the angle x
Step one.
Look at the angle 125. 180-125 will give you the angle on the other side of the line.
Step two add 55+50 and minus the product from 180. this is the upper angle.
Step three add 80+75 then minus that from 180 and that is the angle x
Kindly see the attached pdf. My attempt to solve it, is in it.
I'm wondering if my solution is right. My idea is this: At any point of time, the ball may be assumed to be at an incline which is at an angle of θ(kindly see both the pics in the pdf file). The value of θ will continuously change and so will the value of friction.
I'm not able to figure out, why my solution is wrong, if it is wrong .
TL;DR Summary: I came across this question from a Sri Lankan A-level textbook.
Question - An ice cube with a length of 10 cm is immersed in water at 0 °C. An observer observes the ice cube from the water, and it seems to be 7.75 cm long. If the refractive index of water is 4/3, find the height of the ice cube immersed in the water.
I could not understand how the apparent height of the ice cube in the water depends on the height of the ice cube immersed in the water. Does anyone have an...
Similar threads
- Replies
- 48
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 546
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 382
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 899
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 374
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 956
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 923
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 968
Hot Threads
-
Torque biomechanics
- Started by Naucus
- Replies: 6
- Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Work Done in slowly pulling a thread
- Started by Bling Fizikst
- Replies: 28
- Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
How do you calculate the pull of this piston?
- Started by vdance
- Replies: 27
- Introductory Physics Homework Help
Recent Insights
-
Insights Why Entangled Photon-Polarization Qubits Violate Bell’s Inequality
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 26
- Quantum Interpretations and Foundations
-
Insights Quantum Entanglement is a Kinematic Fact, not a Dynamical Effect
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 11
- Quantum Physics
-
Insights What Exactly is Dirac’s Delta Function? - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 3
- General Math
-
Insights Relativator (Circular Slide-Rule): Simulated with Desmos - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 1
- Special and General Relativity
-
Insights Fixing Things Which Can Go Wrong With Complex Numbers
- Started by PAllen
- Replies: 7
- General Math
-
Insights Fermat's Last Theorem
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 105
- General Math