- #1
argiedude
- 2
- 0
Hi, to all. The FST estimator can tell how different 2 populations are, genetically. The normal FST formula was introduced by Wright and can be found very easily, for example, in wikipedia. But it had some flaws, so it's use has now been completely replaced by the FST estimate introduced by Cockerham and Weir (1984). I've tried very hard to find this formula, but I can't.
This is the original study (it's not public access):
B. S. Weir and C. C. Cockerham.
Estimating f-statistics for the analysis of population structure
Evolution, 38:1358-1370, 1984
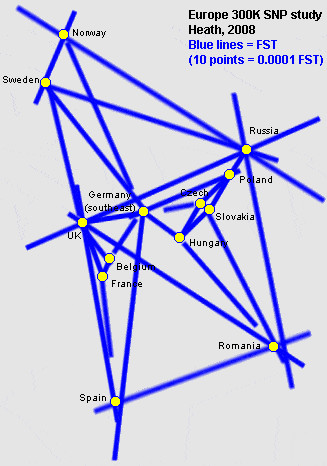
Recent studies, using 100,000's of mutations in the human dna (SNPs), have produced tables of FST distances between several populations. So far this has been done for several European populations (Heath, 2008), and just a few weeks ago a new study came out which included an FST comparison between 20 East Asian populations.
It's all extremely interesting. Here's a graph I made of the genetic distances from the Heath study:
Can you help?
This is the original study (it's not public access):
B. S. Weir and C. C. Cockerham.
Estimating f-statistics for the analysis of population structure
Evolution, 38:1358-1370, 1984
Recent studies, using 100,000's of mutations in the human dna (SNPs), have produced tables of FST distances between several populations. So far this has been done for several European populations (Heath, 2008), and just a few weeks ago a new study came out which included an FST comparison between 20 East Asian populations.
It's all extremely interesting. Here's a graph I made of the genetic distances from the Heath study:
Can you help?