MarkFL
Gold Member
MHB
- 13,284
- 12
Here is the question:
I have posted a link there to this thread so the OP can view my work.
Math help please, I think it about trig.?
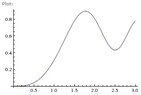
if g(x) = integral from 0 to x (sin(x^2)) on [0,3], then for what value g have a local minimum and for what value of x does g have a local maximum. plot the graph to verify your results.
I have posted a link there to this thread so the OP can view my work.